編輯:關於Android編程
由於直接粘貼復制原因,故直接上傳文檔至此
轉載請注明出處
一.APK的結構以及生成
APK是Android Package的縮寫,即Android application package文件或Android安裝包。每個要安裝到Android平台的應用都要被編譯打包為一個單獨的文件,擴展名為 .apk。APK文件是用編譯器編譯生成的文件包,其中包含了應用的二進制代碼、資源、配置文件等。通過將APK文件直接傳到Android手機中執行即可安裝。APK文件其實就是zip格式,但其擴展名被改為apk。在這裡我們為了詳細講述Android應用程序我們將創建一個永恆的話題, 它就是HelloWorld
程序,在這裡我們創建的Android的HelloWorld程序的目錄結構如下所示:
一個典型的APK文件通常由下列內容組成:
AndroidManifest.xml 程序全局配置文件
classes.dex Dalvik字節碼
resources.arsc 資源索引表, 解壓縮resources.ap_就能看到
res\ 該目錄存放資源文件(圖片,文本,xml布局)
assets\ 該目錄可以存放一些配置文件
src\ java源碼文件
libs\ 存放應用程序所依賴的庫
gen\ 編譯器根據資源文件生成的java文件
bin\ 由編譯器生成的apk文件和各種依賴的資源
META-INF\ 該目錄下存放的是簽名信息
首先來看一下使用Java語言編寫的Android應用程序從源碼到安裝包的整個過程,示意圖如下,其中包含編譯、鏈接和簽名等:
(1). 使用aapt工具將資源文件生成R.java文件, resources.arsc和打包資源文件
(2). 使用aidl工具將.aidl文件編譯成.java文件
(3). 使用javac工具將.java文件編譯成.class文件
(4). 使用dx腳本將眾多.class文件轉換成一個.dex文件
(5). 使用apkbuilder腳本將資源文件和.dex文件生成未簽名的apk安裝文件
(6). 使用jdk中的jarsigner對apk安裝文件進行簽名
上述工具都保存在android-sdk-linux中的tools/和platform-tools文件夾下面.
范例:
src/com.example.helloworldactivity:
package com.example.helloworldactivity;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private final static String TAG = "MainActivity";
private TextView mTextView = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text_view);
Button showButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
showButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
mTextView.setText(R.string.hello_world);
}
});
}
}
res/layout/activity_main.xml:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/show" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="" />
</LinearLayout>
res/values/strings.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="app_name">HelloWorldActivity</string>
<string name="action_settings">Settings</string>
<string name="show">Show</string>
<string name="hello_world">Hello world!</string>
</resources>
AndroidManifest.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.helloworldactivity"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="17" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.helloworldactivity.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
我們前面創建的HelloWorldActivity應用程序資源目錄結構如下所示:
project
接下來,我們在HelloWorldActivity工程目錄下可以使用aapt命令:
aapt p -f -m -J mygen/ -S res/
-I ~/tool/android-sdk-linux/platforms/android-17/android.jar -A assets/
-M AndroidManifest.xml -F helloworldresources.apk
在mygen目錄下生成一個資源ID文件R.java和在當前目錄下生成一個名為helloworldresources.apk的資源包,解壓縮裡面內容如下所示:
被打包的APK資源文件中包含有:資源索引表文件resources.arsc, AndroidManifest.xml二進制文件和res目錄下的應用程序圖片資源及layout目錄下的二進制activity_main.xml文件, res目錄下信息如下所示:
注意:res/values目錄下的字符串信息被編譯進了resources.arsc資源索引文件中,而在R.java文件中僅僅保存了資源ID信息. R.java信息如下所示:
package com.example.helloworldactivity;
public final class R {
public static final class attr {
}
public static final class dimen {
public static final int activity_horizontal_margin=0x7f040000;
public static final int activity_vertical_margin=0x7f040001;
}
public static final class drawable {
public static final int ic_launcher=0x7f020000;
}
public static final class id {
public static final int button=0x7f070000;
public static final int text_view=0x7f070001;
}
public static final class layout {
public static final int activity_main=0x7f030000;
}
public static final class string {
public static final int action_settings=0x7f050001;
public static final int app_name=0x7f050000;
public static final int hello_world=0x7f050003;
public static final int show=0x7f050002;
}
public static final class style {
public static final int AppBaseTheme=0x7f060000;
public static final int AppTheme=0x7f060001;
}
}
下面我們根據分析appt的源碼詳細講述命令:
aapt p -f -m -J mygen/ -S res/
-I ~/tool/android-sdk-linux/platforms/android-17/android.jar -A assets/
-M AndroidManifest.xml -F helloworldresources.apk
是如何將上述應用程序資源編譯生成一個R.java文件, 資源索引表文件resources.arsc, AndroidManifest.xml二進制文件和res目錄下的應用程序圖片資源及layout目錄下的二進制activity_main.xml文件的.
appt入口函數main具體實現如下所示:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/Main.cpp
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
char *prog = argv[0];
Bundle bundle; // 定義一個Bundle類存儲appt命令的各種編譯選項
bool wantUsage = false;
int result = 1; // pessimistically assume an error.
int tolerance = 0;
/* default to compression
** 設置默認的壓縮標准*/
bundle.setCompressionMethod(ZipEntry::kCompressDeflated);
if (argc < 2) {
wantUsage = true;
goto bail;
}
if (argv[1][0] == 'v')
bundle.setCommand(kCommandVersion);
......
else if (argv[1][0] == 'p') // 命令行選項p表示我們要打包資源
bundle.setCommand(kCommandPackage);
......
argc -= 2;
argv += 2;
/*
* Pull out flags. We support "-fv" and "-f -v".
* 一下while循環將各種aapt編譯選項提取出來存放到bundle中 */
while (argc && argv[0][0] == '-') {
/* flag(s) found */
const char* cp = argv[0] +1;
while (*cp != '\0') {
switch (*cp) {
......
case 'f': // 如果編譯出來的文件已經存在,強制覆蓋
bundle.setForce(true); // bundle.mForce(bool)
break;
........
case 'm': // 使生成的包的目錄存放在-J參數指定的目錄
bundle.setMakePackageDirs(true); // bundle.mMakePackageDirs(bool)
break;
......
case 'A': // assert文件夾路徑
argc--;
argv++;
if (!argc) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: No argument supplied for '-A' option\n");
wantUsage = true;
goto bail;
}
convertPath(argv[0]); // 裝換為指定OS的路徑
bundle.setAssetSourceDir(argv[0]); // mAssetSourceDir(const char*)
break;
......
case 'I': // 某個版本平台的android.jar的路徑
argc--;
argv++;
if (!argc) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: No argument supplied for '-I' option\n");
wantUsage = true;
goto bail;
}
convertPath(argv[0]);
// mPackageIncludes.add(file); android::Vector<const char*>
bundle.addPackageInclude(argv[0]);
break;
case 'F': // 具體指定APK文件的輸出
argc--;
argv++;
if (!argc) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: No argument supplied for '-F' option\n");
wantUsage = true;
goto bail;
}
convertPath(argv[0]);
// mOutputAPKFile(const char*)
bundle.setOutputAPKFile(argv[0]);
break;
case 'J': // 指定生成的R.java 的輸出目錄
argc--;
argv++;
if (!argc) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: No argument supplied for '-J' option\n");
wantUsage = true;
goto bail;
}
convertPath(argv[0]);
bundle.setRClassDir(argv[0]); // mRClassDir(const char*)
break;
case 'M': // 指定AndroidManifest.xml文件路徑
argc--;
argv++;
if (!argc) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: No argument supplied for '-M' option\n");
wantUsage = true;
goto bail;
}
convertPath(argv[0]);
// mAndroidMainifestFile(const char*)
bundle.setAndroidManifestFile(argv[0]);
break;
......
case 'S': // res文件夾路徑
argc--;
argv++;
if (!argc) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: No argument supplied for '-S' option\n");
wantUsage = true;
goto bail;
}
convertPath(argv[0]);
// android::Vector<const char*> mResourceSourceDirs;
// mResourceSourceDirs.insertAt(dir,0);
bundle.addResourceSourceDir(argv[0]);
break;
......
default:
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: Unknown flag '-%c'\n", *cp);
wantUsage = true;
goto bail;
}
cp++;
}
argc--;
argv++;
}
/*
* We're past the flags. The rest all goes straight in.
* 設置Bundle的成員變量mArgv和mArgc分別為argv, argc */
bundle.setFileSpec(argv, argc);
/* 通過handleCommand函數來處理指定命令 */
result = handleCommand(&bundle);
bail:
if (wantUsage) {
usage();
result = 2;
}
//printf("--> returning %d\n", result);
return result;
}
處理完aapt的編譯選項之後,接著調用handleCommand函數來處理對應的功能:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/Main.cpp
int handleCommand(Bundle* bundle)
{
......
switch (bundle->getCommand()) {
.......
case kCommandPackage: return doPackage(bundle);
......
default:
fprintf(stderr, "%s: requested command not yet supported\n", gProgName);
return 1;
}
}
最終打包APK的工作由函數doPackage完成,而打包一個應用程序資源的過程非常復雜,我們分如下模塊一一講解:
一. 收錄一個應用程序所有資源文件
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/Command.cpp
/*
* Package up an asset directory and associated application files.
* 打包應用程序中的資源文件 */
int doPackage(Bundle* bundle)
{
const char* outputAPKFile;
int retVal = 1;
status_t err;
sp<AaptAssets> assets;
int N;
FILE* fp;
String8 dependencyFile;
......
// 檢查aapt打包時的參數是否都存在
N = bundle->getFileSpecCount();
if (N < 1 && bundle->getResourceSourceDirs().size() == 0
&& bundle->getJarFiles().size() == 0
&& bundle->getAndroidManifestFile() == NULL
&& bundle->getAssetSourceDir() == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: no input files\n");
goto bail;
}
// 得到最終將資源打包輸出到的APK名稱
outputAPKFile = bundle->getOutputAPKFile();
// Make sure the filenames provided exist and are of the appropriate type.
// 檢查該文件是否存在不存在則創建,並確定其實常規文件
if (outputAPKFile) {
FileType type;
type = getFileType(outputAPKFile);
if (type != kFileTypeNonexistent && type != kFileTypeRegular) {
fprintf(stderr,
"ERROR: output file '%s' exists but is not regular file\n",
outputAPKFile);
goto bail;
}
}
// Load the assets.
// 創建一個AaptAssets對象
assets = new AaptAssets();
......
/* 1.調用AaptAssets類的成員函數slurpFromArgs將AndroidManifest.xml文件,
** 目錄assets和res下的資源目錄和資源文件收錄起來保存到AaptAssets中的
** 成員變量中 */
err = assets->slurpFromArgs(bundle);
if (err < 0) {
goto bail;
}
......
}
AaptAssets的slurpFromArgs函數的具體實現如下所示:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/AaptAssets.cpp
ssize_t AaptAssets::slurpFromArgs(Bundle* bundle)
{
int count;
int totalCount = 0;
FileType type;
// 獲取res目錄的路徑
const Vector<const char *>& resDirs = bundle->getResourceSourceDirs();
const size_t dirCount =resDirs.size();
sp<AaptAssets> current = this;
// 獲取bundle內所保存的aapt的命令選項個數,即要完成的功能個數
const int N = bundle->getFileSpecCount();
/*
* If a package manifest was specified, include that first.
* 如果bundle中指定了AndroidManifest.xml文件,則首先包含它 */
if (bundle->getAndroidManifestFile() != NULL) {
// place at root of zip.
String8 srcFile(bundle->getAndroidManifestFile());
/* 每向AaptAssets的對象中添加一個資源文件或者一個資源目錄都要新建一個
** 類型AaptGroupEntry的空對象並將其添加到一個類型為SortedVector的
** AaptAssets的成員變量mGroupEntries中, 在這裡調用addFile函數是
** 將AndroidManifest.xml文件添加到成員變量mFiles中去.
*/
addFile(srcFile.getPathLeaf(), AaptGroupEntry(), srcFile.getPathDir(),
NULL, String8());
/* 每添加一個資源就加1統計一次 */
totalCount++;
}
/*
* If a directory of custom assets was supplied, slurp 'em up.
* 判斷是否指定了assets文件夾,如果指定則解析它 */
if (bundle->getAssetSourceDir()) {
const char* assetDir = bundle->getAssetSourceDir(); // 獲取目錄名稱
FileType type = getFileType(assetDir); // 獲取目錄類型
if (type == kFileTypeNonexistent) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: asset directory '%s' does not exist\n", assetDir);
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
if (type != kFileTypeDirectory) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: '%s' is not a directory\n", assetDir);
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
String8 assetRoot(assetDir);
/* 創建一個名為”assets”的AaptDir對象 */
sp<AaptDir> assetAaptDir = makeDir(String8(kAssetDir));
AaptGroupEntry group;
/* 調用AaptDir的成員函數slurpFullTree收錄目錄“assets”下的資源文件,
** 並返回資源文件個數 */
count = assetAaptDir->slurpFullTree(bundle, assetRoot, group,
String8(), mFullAssetPaths);
if (count < 0) {
totalCount = count;
goto bail;
}
if (count > 0) {
mGroupEntries.add(group);
}
/* 統計資源文件總個數 */
totalCount += count;
if (bundle->getVerbose())
printf("Found %d custom asset file%s in %s\n",
count, (count==1) ? "" : "s", assetDir);
}
/*
* If a directory of resource-specific assets was supplied, slurp 'em up.
* 收錄指定的res資源目錄下的資源文件 */
for (size_t i=0; i<dirCount; i++) {
const char *res = resDirs[i];
if (res) {
type = getFileType(res); // 獲取文件類型
if (type == kFileTypeNonexistent) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: resource directory '%s' does not exist\n", res);
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
if (type == kFileTypeDirectory) {
// 如果指定了多個res資源目錄文件, 則為其創建多個AaptAssets
// 類來分別收錄這些目錄中的信息,並將其設置賦值給當前
// AaptAssets對象的成員變量mOverlay
if (i>0) {
sp<AaptAssets> nextOverlay = new AaptAssets();
current->setOverlay(nextOverlay);
current = nextOverlay;
current->setFullResPaths(mFullResPaths);
}
// 調用成員函數slurpResourceTree來收錄res目錄下的資源文件
count = current->slurpResourceTree(bundle, String8(res));
if (count < 0) {
totalCount = count;
goto bail;
}
totalCount += count; // 統計資源文件個數
}
else {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: '%s' is not a directory\n", res);
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
}
}
/*
* Now do any additional raw files.
* 接著收錄剩余的指定的資源文件 */
for (int arg=0; arg<N; arg++) {
const char* assetDir = bundle->getFileSpecEntry(arg);
FileType type = getFileType(assetDir);
if (type == kFileTypeNonexistent) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: input directory '%s' does not exist\n", assetDir);
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
if (type != kFileTypeDirectory) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: '%s' is not a directory\n", assetDir);
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
String8 assetRoot(assetDir);
if (bundle->getVerbose())
printf("Processing raw dir '%s'\n", (const char*) assetDir);
/*
* Do a recursive traversal of subdir tree. We don't make any
* guarantees about ordering, so we're okay with an inorder search
* using whatever order the OS happens to hand back to us.
*/
count = slurpFullTree(bundle,
assetRoot, AaptGroupEntry(), String8(), mFullAssetPaths);
if (count < 0) {
/* failure; report error and remove archive */
totalCount = count;
goto bail;
}
totalCount += count;
if (bundle->getVerbose())
printf("Found %d asset file%s in %s\n",
count, (count==1) ? "" : "s", assetDir);
}
count = validate();
if (count != NO_ERROR) {
totalCount = count;
goto bail;
}
count = filter(bundle);
if (count != NO_ERROR) {
totalCount = count;
goto bail;
}
bail:
return totalCount;
}
AaptAssets的成員函數addFile用來向AaptAssets的一個對象添加一個資源文件到其成員變量mFiles中去或者添加一個資源目錄到其成員變量mDirs中去, 注意:每一個資源文件都封裝成一個AaptFile類然後用AaptGroup將這些AaptFile對象組織起來,其具體實現如下所示:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/AaptAssets.cpp
sp<AaptFile> AaptAssets::addFile(
const String8& filePath, const AaptGroupEntry& entry,
const String8& srcDir, sp<AaptGroup>* outGroup,
const String8& resType)
{
sp<AaptDir> dir = this; // AaptAssets類繼承了一個AaptDir類
sp<AaptGroup> group;
sp<AaptFile> file;
String8 root, remain(filePath), partialPath;
while (remain.length() > 0) {
// 獲取remain所描述文件的工作目錄,如果其僅僅指定了文件名則返回文件名,
// 如果文件名前添加了路徑,則返回最上層的目錄名
// 例如,remain = “AndroidManifest.xml”,則root=“AndroidManifest.xml”,
// remain = “”; 如果remain=“/rootpath/subpath/AndroidManifest.xml”,
// 則,root=“rootpath”, remain=”subpath/AndroidManifest.xml”
root = remain.walkPath(&remain);
partialPath.appendPath(root);
const String8 rootStr(root);
/* 在這裡remain.length()返回0 */
if (remain.length() == 0) { // 添加資源文件到mFiles中去
/* dir指向當前AaptAssets對象,其調用getFiles返回類型為
** DefaultKeyVector<String8, sp<AaptGroup>>成員變量mFiles,判斷其內部
** 是否包含了名稱為rootStr的AaptGroup對象,並返回其位置值 */
ssize_t i = dir->getFiles().indexOfKey(rootStr);
/* 如果返回的位置值>=0表示mFiles中已經包含了這個名為rootStr的
** AaptGroup對象,則將group指向該對象, 否則新建一個名稱為rootStr
** 的AaptGroup對象並添加到mFiles中去 */
if (i >= 0) {
group = dir->getFiles().valueAt(i);
} else {
group = new AaptGroup(rootStr, filePath);
status_t res = dir->addFile(rootStr, group);
if (res != NO_ERROR) {
return NULL;
}
}
// 新建一個AaptFile對象指向需要添加的源文件, 並將該AaptFile對象
// 添加到類型為DefaultKeyedVector<AaptGroupEntry, sp<AaptFile> >的
// AaptGroup的成員變量 mFiles中去
file = new AaptFile(srcDir.appendPathCopy(filePath), entry, resType);
status_t res = group->addFile(file);
if (res != NO_ERROR) {
return NULL;
}
break;
} else { // 添加資源目錄到mDirs中去
/* dir指向當前AaptAssets對象,其調用getDirs返回類型為
** DefaultKeyVector<String8, sp<AaptDir>>成員變量mDirs,判斷其內部
** 是否包含了名稱為rootStr的AaptDir對象,並返回其位置值 */
ssize_t i = dir->getDirs().indexOfKey(rootStr);
/* 如果返回的位置值>=0表示mDirs中已經包含了這個名為rootStr的
** AaptDir對象,則將dir指向該對象,否則新建一個名稱為rootStr
** 的AaptDir對象並添加到mDirs中去 */
if (i >= 0) {
dir = dir->getDirs().valueAt(i);
} else {
sp<AaptDir> subdir = new AaptDir(rootStr, partialPath);
status_t res = dir->addDir(rootStr, subdir);
if (res != NO_ERROR) {
return NULL;
}
dir = subdir;
}
}
}
/* 將一個空的AaptGroupEntry對象添加到mGroupEntries中去,其是一個SortedVector
*/
mGroupEntries.add(entry);
if (outGroup) *outGroup = group;
return file;
}
AaptAssets的成員函數slurpFullTree將會收錄路徑名為srcDir目錄下的所有資源文件,並將對應目錄下的文件名都保存到fullResPaths中去,其具體實現如下所示:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/AaptAssets.cpp
ssize_t AaptAssets::slurpFullTree(Bundle* bundle, const String8& srcDir,
const AaptGroupEntry& kind,
const String8& resType,
sp<FilePathStore>& fullResPaths)
{
/* 接著調用父類中的AaptDir的成員函數slurpFullTree收錄srcDir中的
** 資源文件 */
ssize_t res = AaptDir::slurpFullTree(bundle, srcDir, kind, resType, fullResPaths);
/* 如果收錄的資源個數>0,則將其歸為一類,為這類資源文件創建一個對應
** AaptGroupEntry對象並添加到對應的成員變量mGroupEntries中去 */
if (res > 0) {
mGroupEntries.add(kind);
}
return res;
}
ssize_t AaptDir::slurpFullTree(Bundle* bundle, const String8& srcDir,
const AaptGroupEntry& kind, const String8& resType,
sp<FilePathStore>& fullResPaths)
{
Vector<String8> fileNames;
{
DIR* dir = NULL;
/* 首先打開將要收錄的資源文件所在的源目錄 */
dir = opendir(srcDir.string());
if (dir == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: opendir(%s): %s\n", srcDir.string(), strerror(errno));
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
/*
* Slurp the filenames out of the directory.
* 遍歷srcDir目錄下的每一個資源文件,將其添加到AaptAssets的成員變量
* mFullAssetPaths中,其繼承了一個Vector<String8> */
while (1) {
struct dirent* entry;
entry = readdir(dir);
if (entry == NULL)
break;
if (isHidden(srcDir.string(), entry->d_name))
continue;
String8 name(entry->d_name);
fileNames.add(name);
// Add fully qualified path for dependency purposes
// if we're collecting them
// 按照全部路徑將資源文件添加到fullResPaths中去
if (fullResPaths != NULL) {
fullResPaths->add(srcDir.appendPathCopy(name));
}
}
closedir(dir);
}
ssize_t count = 0;
/*
* Stash away the files and recursively descend into subdirectories.
* 遞歸解析srcDir下的子目錄中的資源文件,指導收錄完所有的
* 目錄中的資源文件為止 */
const size_t N = fileNames.size();
size_t i;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String8 pathName(srcDir);
FileType type;
pathName.appendPath(fileNames[i].string());
type = getFileType(pathName.string());
/* 如果是資源子目錄,並且其尚未收錄在mDirs中,則為其創建一個
** AaptDir對象,繼續遞歸遍歷其中的資源文件及目錄 */
if (type == kFileTypeDirectory) {
sp<AaptDir> subdir;
bool notAdded = false;
/* 如果*/
if (mDirs.indexOfKey(fileNames[i]) >= 0) {
subdir = mDirs.valueFor(fileNames[i]);
} else {
subdir =
new AaptDir(fileNames[i], mPath.appendPathCopy(fileNames[i]));
notAdded = true;
}
ssize_t res = subdir->slurpFullTree(bundle, pathName, kind,
resType, fullResPaths);
if (res < NO_ERROR) {
return res;
}
if (res > 0 && notAdded) {
mDirs.add(fileNames[i], subdir); // 將資源目錄添加到mDirs變量中
}
count += res;
/* 如果其為一個資源文件,則為其創建一個指定的AaptFile變量
** 並為其創建一個對應的AaptGroup變量, 將這個AaptGroup變量添加
** 到mFiles變量中,然後將AaptFile變量添加到AaptGroup中去 */
} else if (type == kFileTypeRegular) {
sp<AaptFile> file = new AaptFile(pathName, kind, resType);
status_t err = addLeafFile(fileNames[i], file);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
return err;
}
count++;
} else {
if (bundle->getVerbose())
printf(" (ignoring non-file/dir '%s')\n", pathName.string());
}
}
/* 返回總的資源文件個數 */
return count;
}
AaptAssets的成員函數slurpResourceTree將會收錄路徑名為srcDir目錄下的所有資源文件,該函數具體實現如下所示:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/AaptAssets.cpp
ssize_t AaptAssets::slurpResourceTree(Bundle* bundle, const String8& srcDir)
{
ssize_t err = 0;
/* 打開資源文件夾 */
DIR* dir = opendir(srcDir.string());
if (dir == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: opendir(%s): %s\n", srcDir.string(), strerror(errno));
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
status_t count = 0;
/*
* Run through the directory, looking for dirs that match the
* expected pattern.
* 遞歸遍歷對應的資源文件夾 */
while (1) {
struct dirent* entry = readdir(dir);
if (entry == NULL) {
break;
}
if (isHidden(srcDir.string(), entry->d_name)) {
continue;
}
String8 subdirName(srcDir);
subdirName.appendPath(entry->d_name);
AaptGroupEntry group;
String8 resType;
/* 調用AaptGroupEntry類的initFromDirName函數來歸類子目錄下的資源文件
** 並將對應的資源文件類型通過resType返回
** 按照這樣的順序: mcc, mnc, loc, layoutsize, layoutlong, orient, den,touch,
** key, keysHidden, nav, navHidden, size, vers, uiModeType, uiModeNight,
** smallestwidthdp, widthdp, heightdp收錄對應的資源文件名稱將其分類
** 保存到group變量中, 這個函數很簡單就不具體分析 */
bool b = group.initFromDirName(entry->d_name, &resType);
if (!b) {
fprintf(stderr, "invalid resource directory name: %s/%s\n", srcDir.string(),
entry->d_name);
err = -1;
continue;
}
......
FileType type = getFileType(subdirName.string());
/* 如果是一個子目錄文件, 則為其創建一個對應的AaptDir對象,並調用
** 該對象的成員函數slurpFullTree收錄該子目錄下的所有資源文件 */
if (type == kFileTypeDirectory) {
sp<AaptDir> dir = makeDir(resType);
ssize_t res = dir->slurpFullTree(bundle, subdirName, group,
resType, mFullResPaths);
if (res < 0) {
count = res;
goto bail;
}
if (res > 0) {
mGroupEntries.add(group);
count += res;
}
// Only add this directory if we don't already have a resource dir
// for the current type. This ensures that we only add the dir once
// for all configs.
// 判斷是否添加過對應的資源目錄到成員變量mResDirs中了
// 如果沒有添加過則將其添加進去
sp<AaptDir> rdir = resDir(resType);
if (rdir == NULL) {
mResDirs.add(dir);
}
} else {
if (bundle->getVerbose()) {
fprintf(stderr, " (ignoring file '%s')\n", subdirName.string());
}
}
}
bail:
closedir(dir);
dir = NULL;
if (err != 0) {
return err;
}
return count;
}
二. 編譯AndroidManifest.xml文件和res目錄下資源文件
以上通過AaptAssets類的成員函數slurpFromArgs將一個應用程序中的所有資源文件收錄完成以後,接下來就要調用buildResources函數編譯AndroidManifest.xml文件以及res目錄下的資源文件,這些資源文件的路徑等詳細信息保存在AaptAssets對象assets中,具體實現如下所示:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/Command.cpp
/*
* Package up an asset directory and associated application files.
* 打包應用程序中的資源文件 */
int doPackage(Bundle* bundle)
{
const char* outputAPKFile;
int retVal = 1;
status_t err;
sp<AaptAssets> assets;
int N;
FILE* fp;
String8 dependencyFile;
......
// If they asked for any fileAs that need to be compiled, do so.
// 編譯res目錄下資源文件以及AndroidManifest.xml文件
if (bundle->getResourceSourceDirs().size() || bundle->getAndroidManifestFile()) {
err = buildResources(bundle, assets);
if (err != 0) {
goto bail;
}
}
......
}
將文本xml資源文件編譯成二進制資源文件的方法buildResources函數的具體實現如下所示,由於這個函數非常長,所以我們分開來對其一一進行解析:
1. 編譯AndroidManifest.xml文件
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/Resource.cpp
status_t buildResources(Bundle* bundle, const sp<AaptAssets>& assets)
{
// First, look for a package file to parse. This is required to
// be able to generate the resource information.
// 首先從assets中獲取AndroidManifest.xml文件的信息
// AndroidManifest.xml文件信息是保存在assets的成員變量mFiles中的,
// 但是其被封裝成一個AaptFile類對象保存在AaptGroup對象最終再
// 保存到mFiles中的
sp<AaptGroup> androidManifestFile =
assets->getFiles().valueFor(String8("AndroidManifest.xml"));
if (androidManifestFile == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: No AndroidManifest.xml file found.\n");
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
// 調用parsePackage函數解析AndroidManifest.xml文件
status_t err = parsePackage(bundle, assets, androidManifestFile);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
return err;
}
......
}
parsePackage函數的具體實現如下所示, 這個解析過程我們對應著AndroidManifest.xml文件看, 具體實現如下所示:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/Resource.cpp
static status_t parsePackage(Bundle* bundle, const sp<AaptAssets>& assets,
const sp<AaptGroup>& grp)
{
// 以下代碼確保只有一個AndroidManifest.xml文件
if (grp->getFiles().size() != 1) {
fprintf(stderr, "warning: Multiple AndroidManifest.xml files found, using %s\n",
grp->getFiles().valueAt(0)->getPrintableSource().string());
}
// 取出存放AndroidManifest.xml文件信息的AaptFile對象
sp<AaptFile> file = grp->getFiles().valueAt(0);
// 定義一個ResXMLTree對象,然後調用parseXMLResource來詳細解析
// AndroidManifest.xml文件
// 這個函數主要完成三個工作:
// 1. 收集file文件指向的xml文件中字符串資源信息.
// 2. 壓平該file文件只想的xml文件中資源信息
// 3. 將前兩步組織的到的資源信息最終組織到一個ResXMLTree所描述的數據結構中.
ResXMLTree block;
status_t err = parseXMLResource(file, &block);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
return err;
}
//printXMLBlock(&block);
ResXMLTree::event_code_t code;
while ((code=block.next()) != ResXMLTree::START_TAG
&& code != ResXMLTree::END_DOCUMENT
&& code != ResXMLTree::BAD_DOCUMENT) {
}
size_t len;
if (code != ResXMLTree::START_TAG) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s:%d: No start tag found\n",
file->getPrintableSource().string(), block.getLineNumber());
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
if (strcmp16(block.getElementName(&len), String16("manifest").string()) != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s:%d: Invalid start tag %s, expected <manifest>\n",
file->getPrintableSource().string(), block.getLineNumber(),
String8(block.getElementName(&len)).string());
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
ssize_t nameIndex = block.indexOfAttribute(NULL, "package");
if (nameIndex < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s:%d: <manifest> does not have package attribute.\n",
file->getPrintableSource().string(), block.getLineNumber());
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
assets->setPackage(String8(block.getAttributeStringValue(nameIndex, &len)));
String16 uses_sdk16("uses-sdk");
while ((code=block.next()) != ResXMLTree::END_DOCUMENT
&& code != ResXMLTree::BAD_DOCUMENT) {
if (code == ResXMLTree::START_TAG) {
if (strcmp16(block.getElementName(&len), uses_sdk16.string()) == 0) {
ssize_t minSdkIndex =
block.indexOfAttribute(RESOURCES_ANDROID_NAMESPACE,
"minSdkVersion");
if (minSdkIndex >= 0) {
const uint16_t* minSdk16 =
block.getAttributeStringValue(minSdkIndex, &len);
const char* minSdk8 = strdup(String8(minSdk16).string());
bundle->setManifestMinSdkVersion(minSdk8);
}
}
}
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
parseXMLResource函數的具體實現如下所示, 下面我們就一一解析其是如何解析一個XML資源文件的:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/XMLNode.cpp
status_t parseXMLResource(const sp<AaptFile>& file, ResXMLTree* outTree,
bool stripAll, bool keepComments,
const char** cDataTags)
{
/* 接著調用XMLNode的成員函數parse來解析AndroidManifest.xml文件 */
sp<XMLNode> root = XMLNode::parse(file);
if (root == NULL) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
root->removeWhitespace(stripAll, cDataTags);
/* 新建一個AaptFile作為輸出文件 */
sp<AaptFile> rsc = new AaptFile(String8(), AaptGroupEntry(), String8());
/* 調用flatten函數壓平AndroidManifest.xml文件, 將壓平後的xml文件信息按指定
** 格式組織在rsc的數據緩沖區中 */
status_t err = root->flatten(rsc, !keepComments, false);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
return err;
}
err = outTree->setTo(rsc->getData(), rsc->getSize(), true);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
return err;
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
(1). 收集XML文本文件信息
收集AdaptFile對象file所指向的xml文本文件中信息, 將其組織在一個以XMLNode對象root為根的樹中
sp<XMLNode> XMLNode::parse(const sp<AaptFile>& file)
{
char buf[16384];
/* 以只讀方式打開AndroidManifest.xml文件 */
int fd = open(file->getSourceFile().string(), O_RDONLY | O_BINARY);
if (fd < 0) {
SourcePos(file->getSourceFile(), -1).error("Unable to open file for read: %s",
strerror(errno));
return NULL;
}
/* 創建一個XML文件解析器, 該解析器是定義在expat庫中的
** Expat 是一個用C語言開發的、用來解析XML文檔的開發庫,它最初是開源的、
** Mozilla 項目下的一個XML解析器。采用流的方式來解析XML文件,並且基於
** 事件通知型來調用分析到的數據,並不需要把所有XML文件全部加載到內存裡,
** 這樣可以分析非常大的XML文件。*/
/* 1.創建一個XML分析器。*/
XML_Parser parser = XML_ParserCreateNS(NULL, 1);
ParseState state;
state.filename = file->getPrintableSource(); // 制定文件名稱為AndroidManifest.xml
state.parser = parser;
XML_SetUserData(parser, &state); // 設置用戶數據
/* 2.第一個參數是那個Parser句柄,第二個和第三個參數則是整個Parser的核心,
** 類型為CallBack的函數
*/
XML_SetElementHandler(parser, startElement, endElement);
/* startNamespace: 解析xmlns:android開頭的信息:
** 參數: prefix = android, uri= android右邊的屬性值信息
** "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
** endNamespace - 銷毀ParseState中緩存的數據
** 這個特殊的xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
** 屬性名和屬性值會創建一個XMLNode作為根節點, 其也叫做命名空間
** 解析命名空間和標簽元素類似,就不再贅述 */
XML_SetNamespaceDeclHandler(parser, startNamespace, endNamespace);
/* 函數是設置處理一個<>和</>之間的字段的回調
** <Item>This is a normal text</Item>
** 那麼字符串“This is a normal text”就稱為一個CDATA */
XML_SetCharacterDataHandler(parser, characterData);
/* 處理注釋的函數 */
XML_SetCommentHandler(parser, commentData);
ssize_t len;
bool done;
do {
len = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
done = len < (ssize_t)sizeof(buf);
if (len < 0) {
close(fd);
return NULL;
}
/* 第二個參數是用戶指定的Buffer指針, 第三個是這塊Buffer中實際內容的
** 字節數,最後參數代表是否這塊Buffer已經結束。比如要解析的XML文件太大,
** 但內存比較吃緊,Buffer比較小,則可以循環讀取文件,然後丟給Parser,
** 在文件讀取結束前,isFinal參數為FALSE,反之為TRUE。 */
if (XML_Parse(parser, buf, len, done) == XML_STATUS_ERROR) {
close(fd);
return NULL;
}
} while (!done);
XML_ParserFree(parser); // 銷毀一個解析器
if (state.root == NULL) {
SourcePos(file->getSourceFile(), -1).error("No XML data generated when parsing");
}
close(fd);
return state.root;
}
/* startElement解析:<> 或者 </>中的信息,
** 參數:name為標簽名, atts - 從左到右將保存=兩邊屬性名和屬性值.
** endElement解析: </> 中的信息*/
void XMLCALL
XMLNode::startElement(void *userData, const char *name, const char **atts)
{
NOISY_PARSE(printf("Start Element: %s\n", name));
printf("Start Element: %s\n", name);
ParseState* st = (ParseState*)userData;
String16 ns16, name16;
splitName(name, &ns16, &name16);
/* 為每一個名稱為name的標簽創建一個XMLNode對象 */
sp<XMLNode> node = XMLNode::newElement(st->filename, ns16, name16);
/* 設置標簽開始的行號 */
node->setStartLineNumber(XML_GetCurrentLineNumber(st->parser));
if (st->pendingComment.size() > 0) {
node->appendComment(st->pendingComment);
st->pendingComment = String16();
}
if (st->stack.size() > 0) {
/** 而name子標簽作為name標簽XMLNode對象的一個
** 子對象保存到XMLNode的成員變量mChildren(Vector)中, 而ParseState
** 只是用於緩存XMLNode數據信息用,緩存完成之後隨即在endElement函數
** 中銷毀.
st->stack.itemAt(st->stack.size()-1)->addChild(node);
} else {
st->root = node; // 根節點是命名空間節點
}
st->stack.push(node); // 緩存
for (int i = 0; atts[i]; i += 2) {
splitName(atts[i], &ns16, &name16);
printf(" attrs: %s=%s\n", atts[i], atts[i+1]);
node->addAttribute(ns16, name16, String16(atts[i+1]));
}
}
void XMLCALL
XMLNode::endElement(void *userData, const char *name)
{
NOISY_PARSE(printf("End Element: %s\n", name));
printf("End Element: %s\n", name);
ParseState* st = (ParseState*)userData;
sp<XMLNode> node = st->stack.itemAt(st->stack.size()-1);
/* 設置標簽結束行號 */
node->setEndLineNumber(XML_GetCurrentLineNumber(st->parser));
if (st->pendingComment.size() > 0) {
node->appendComment(st->pendingComment);
st->pendingComment = String16();
}
String16 ns16, name16;
splitName(name, &ns16, &name16);
st->stack.pop();
}
/* 成員函數addAttribute將所有屬性名和屬性值的信息添加到其保存屬性信息的
** 成員變量mAttributes和mAttributeOrder中,每一個屬性的信息會被保存在一個
** attribute_entry的結構體中,默認為每一個屬性所分配的資源ID是0.
*/
status_t XMLNode::addAttribute(const String16& ns, const String16& name,
const String16& value)
{
if (getType() == TYPE_CDATA) {
SourcePos(mFilename, getStartLineNumber()).error("Child to CDATA node.");
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
if (ns != RESOURCES_TOOLS_NAMESPACE) {
attribute_entry e;
e.index = mNextAttributeIndex++;
e.ns = ns;
e.name = name; // 屬性名
e.string = value; // 屬性值
mAttributes.add(e);
mAttributeOrder.add(e.index, mAttributes.size()-1);
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
(2). 壓平收集完字符串信息的XML文本文件
至此,解析完一個xml文本文件之後接著調用XMLNode成員函數flatten來壓平該文件,下面我們一一解析這個flatten過程:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/XMLNode.cpp
status_t XMLNode::flatten(const sp<AaptFile>& dest,
bool stripComments, bool stripRawValues) const
{
/* 創建一個字符串池StringPool變量strings 保存屬性名稱字符串 */
StringPool strings(mUTF8);
Vector<uint32_t> resids; // 保存屬性名的資源ID號
// First collect just the strings for attribute names that have a
// resource ID assigned to them. This ensures that the resource ID
// array is compact, and makes it easier to deal with attribute names
// in different namespaces (and thus with different resource IDs).
// 首先收集屬性名字符串,這些字符串有一個資源ID指向它們.
// 這確保資源ID數組緊湊的,並且不同於命名空間的資源ID,
// 這使得處理屬性名變得更簡單
// 注意:在這裡實際上什麼工作都沒有做!!FUCK
collect_resid_strings(&strings, &resids);
// Next collect all remainibng strings.
// 真正的收集工作在這裡才工作,上面什麼工作都沒做還遞歸遍歷半天
collect_strings(&strings, &resids, stripComments, stripRawValues);
......
}
/* 該函數從指向命名空間的root XMLNode開始遞歸遍歷收集每一個標簽(
** 一個標簽中的屬性信息保存在一個XMLNode變量中)的屬性名和ID
*/
status_t XMLNode::collect_resid_strings(StringPool* outPool,
Vector<uint32_t>* outResIds) const
{
/* 真正收集XML文件中一個標簽的屬性名稱和其ID號的工作
** 在函數collect_attr_strings中完成, 這裡不工作 */
collect_attr_strings(outPool, outResIds, false);
const int NC = mChildren.size();
for (int i=0; i<NC; i++) {
mChildren.itemAt(i)->collect_resid_strings(outPool, outResIds);
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
status_t XMLNode::collect_strings(StringPool* dest, Vector<uint32_t>* outResIds,
bool stripComments, bool stripRawValues) const
{
/* 真正收集XML文件中一個標簽的屬性名稱和其ID號的工作
** 在函數collect_attr_strings中完成, 這裡工作 */
collect_attr_strings(dest, outResIds, true);
/* 下列代碼在收集完屬性名稱之後,接著將對應的其它信息按照
** 一定的順序收集保存到字符串資源池 */
int i;
if (RESOURCES_TOOLS_NAMESPACE != mNamespaceUri) {
if (mNamespacePrefix.size() > 0) {
dest->add(mNamespacePrefix, true);
}
if (mNamespaceUri.size() > 0) {
dest->add(mNamespaceUri, true);
}
}
if (mElementName.size() > 0) {
dest->add(mElementName, true);
}
if (!stripComments && mComment.size() > 0) {
dest->add(mComment, true);
}
const int NA = mAttributes.size();
for (i=0; i<NA; i++) {
const attribute_entry& ae = mAttributes.itemAt(i);
if (ae.ns.size() > 0) {
dest->add(ae.ns, true);
}
if (!stripRawValues || ae.needStringValue()) {
dest->add(ae.string, true);
}
/*
if (ae.value.dataType == Res_value::TYPE_NULL
|| ae.value.dataType == Res_value::TYPE_STRING) {
dest->add(ae.string, true);
}
*/
}
if (mElementName.size() == 0) {
// If not an element, include the CDATA, even if it is empty.
dest->add(mChars, true);
}
const int NC = mChildren.size();
for (i=0; i<NC; i++) {
mChildren.itemAt(i)->collect_strings(dest, outResIds,
stripComments, stripRawValues);
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
/* 收集XML文件中一個標簽中的屬性名稱及其ID分別保存到字符串資源池和ID池中 */
status_t XMLNode::collect_attr_strings(StringPool* outPool,
Vector<uint32_t>* outResIds, bool allAttrs) const {
/* 獲取屬性個數 */
const int NA = mAttributes.size();
for (int i=0; i<NA; i++) {
/* 每一個屬性使用一個attribute_entry結構體來表示 */
const attribute_entry& attr = mAttributes.itemAt(i);
// 獲取資源屬性ID,默認的資源屬性ID為0
// 故,在這裡該函數什麼工作都沒有做
uint32_t id = attr.nameResId;
if (id || allAttrs) {
// See if we have already assigned this resource ID to a pooled
// string...
// 檢測在字符串池中是否已經收集到了指定屬性名稱的字符串
const Vector<size_t>* indices = outPool->offsetsForString(attr.name);
ssize_t idx = -1;
if (indices != NULL) {
const int NJ = indices->size();
const size_t NR = outResIds->size();
for (int j=0; j<NJ; j++) {
size_t strIdx = indices->itemAt(j);
if (strIdx >= NR) {
if (id == 0) {
// We don't need to assign a resource ID for this one.
idx = strIdx;
break;
}
// Just ignore strings that are out of range of
// the currently assigned resource IDs... we add
// strings as we assign the first ID.
} else if (outResIds->itemAt(strIdx) == id) {
idx = strIdx;
break;
}
}
}
if (idx < 0) {
// 尚未將指定的屬性名添加到字符串資源池中,如果add函數後面跟隨
// 著描述字符串屬性的entry_style_span的Vector則將字符串屬性一並
// 加入, 並返回其在字符串資源池中位置
idx = outPool->add(attr.name);
// 判斷是否為屬性名分配過資源ID
if (id != 0) {
/* 確保屬性名資源ID與屬性名對應 */
while ((ssize_t)outResIds->size() <= idx) {
outResIds->add(0);
}
// 替換原有資源ID
outResIds->replaceAt(id, idx);
}
}
attr.namePoolIdx = idx;
}
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
為收集到的字符串信息分配字符串資源池並將收集到的信息按照指定格式組織起來,在介紹字符串緩沖塊之前,我們首先了解下StringPool的幾個重要的成員變量的含義:
// The following data structures represent the actual structures
// that will be generated for the final string pool.
// Raw array of unique strings, in some arbitrary order. This is the
// actual strings that appear in the final string pool, in the order
// that they will be written.
// mEntries用於保存屬性字符串信息, 每一個字符串都會被封裝成一個
// struct entry,這個結構體保存了這個字符串的各種配置屬性, 每次將
// 一個字符串信息add到StringPool中時都要將其封裝成一個entry
// 然後add到mEntries中
// 注意: 每一個entry結構體的indices這個Vector中保存著這個字符串在
// mValues中的位置值
Vector<entry> mEntries;
// Array of indices into mEntries, in the order they were
// added to the pool. This can be different than mEntries
// if the same string was added multiple times (it will appear
// once in mEntries, with multiple occurrences in this array).
// This is the lookup array that will be written for finding
// the string for each offset/position in the string pool.
// mEntryArray中保存著某一個字符串在mEntries中的位置
Vector<size_t> mEntryArray;
// Optional style span information associated with each index of
// mEntryArray.
// mEntryStyleArray中保存著mValues中的字符串的樣式,其跟
// mValues中的字符串是一一對應的
Vector<entry_style> mEntryStyleArray;
// The following data structures are used for book-keeping as the
// string pool is constructed.
// Unique set of all the strings added to the pool, mapped to
// the first index of mEntryArray where the value was added.
// mValues保存著一個字符串的值以及其在mValues中的位置值
DefaultKeyedVector<String16, ssize_t> mValues;
下面我們詳細介紹是如何為一個StringPool創建一個StringBlock來組織存儲在其中的字符串信息的,具體實現如下所示:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/XMLNode.cpp
status_t XMLNode::flatten(const sp<AaptFile>& dest,
bool stripComments, bool stripRawValues) const
{
StringPool strings(mUTF8);
Vector<uint32_t> resids;
......
/* 收集到的屬性信息都保存在strings所指向的字符串資源池
** 現在為這些字符串資源池中的屬性信息分配字符串塊 */
sp<AaptFile> stringPool = strings.createStringBlock();
......
}
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/StringPool.cpp
sp<AaptFile> StringPool::createStringBlock()
{
/* 首先創建一個匿名AaptFile類對象 */
sp<AaptFile> pool = new AaptFile(String8(), AaptGroupEntry(),
String8());
/* 調用writeStringBlock來創建字符串塊 */
status_t err = writeStringBlock(pool);
return err == NO_ERROR ? pool : NULL;
}
status_t StringPool::writeStringBlock(const sp<AaptFile>& pool)
{
......
// First we need to add all style span names to the string pool.
// We do this now (instead of when the span is added) so that these
// will appear at the end of the pool, not disrupting the order
// our client placed their own strings in it.
/* 計算存儲字符串樣式的Vector大小及其設置一些成員變量 */
const size_t STYLES = mEntryStyleArray.size();
size_t i;
for (i=0; i<STYLES; i++) {
entry_style& style = mEntryStyleArray.editItemAt(i);
const size_t N = style.spans.size();
for (size_t i=0; i<N; i++) {
entry_style_span& span = style.spans.editItemAt(i);
ssize_t idx = add(span.name, true);
if (idx < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error adding span for style tag '%s'\n",
String8(span.name).string());
return idx;
}
span.span.name.index = (uint32_t)idx;
}
}
/* 計算mEntryArray的大小 */
const size_t ENTRIES = mEntryArray.size();
// Now build the pool of unique strings.
/* 計算mEntries的大小, 也就是字符串個數 */
const size_t STRINGS = mEntries.size();
/* 計算出預分配內存緩沖區大小 */
const size_t preSize = sizeof(ResStringPool_header) // header
+ (sizeof(uint32_t)*ENTRIES) // 字符串偏移數組
+ (sizeof(uint32_t)*STYLES); // 格式偏移數組
/* 調用AaptFile的成員函數editData函數分配指定大小的內存緩沖區 */
if (pool->editData(preSize) == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: Out of memory for string pool\n");
return NO_MEMORY;
}
/* 判斷字符格式 */
const size_t charSize = mUTF8 ? sizeof(uint8_t) : sizeof(char16_t);
/* 下列代碼詳細計算沒一個字符串大小並為其分配內存空間並將StringPool中的
** 字符串按照二進制格式拷貝到StringBlock中為其分配的空間中 */
size_t strPos = 0;
for (i=0; i<STRINGS; i++) {
entry& ent = mEntries.editItemAt(i);
const size_t strSize = (ent.value.size());
const size_t lenSize = strSize > (size_t)(1<<((charSize*8)-1))-1 ?
charSize*2 : charSize;
String8 encStr;
if (mUTF8) {
encStr = String8(ent.value);
}
const size_t encSize = mUTF8 ? encStr.size() : 0;
const size_t encLenSize = mUTF8 ?
(encSize > (size_t)(1<<((charSize*8)-1))-1 ?
charSize*2 : charSize) : 0;
ent.offset = strPos; // 計算字符串偏移量,以文件開頭偏移量為0, 以此類推
const size_t totalSize = lenSize + encLenSize +
((mUTF8 ? encSize : strSize)+1)*charSize;
void* dat = (void*)pool->editData(preSize + strPos + totalSize);
if (dat == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: Out of memory for string pool\n");
return NO_MEMORY;
}
dat = (uint8_t*)dat + preSize + strPos;
if (mUTF8) {
uint8_t* strings = (uint8_t*)dat;
ENCODE_LENGTH(strings, sizeof(uint8_t), strSize)
ENCODE_LENGTH(strings, sizeof(uint8_t), encSize)
strncpy((char*)strings, encStr, encSize+1);
} else {
uint16_t* strings = (uint16_t*)dat;
ENCODE_LENGTH(strings, sizeof(uint16_t), strSize)
strcpy16_htod(strings, ent.value);
}
strPos += totalSize;
}
// Pad ending string position up to a uint32_t boundary.
// 將StringBlock內存對齊
if (strPos&0x3) {
size_t padPos = ((strPos+3)&~0x3);
uint8_t* dat = (uint8_t*)pool->editData(preSize + padPos);
if (dat == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: Out of memory padding string pool\n");
return NO_MEMORY;
}
memset(dat+preSize+strPos, 0, padPos-strPos);
strPos = padPos;
}
// Build the pool of style spans.
// 在隨後的StringBlock中將字符串格式按照二進制格式存儲起來
size_t styPos = strPos;
for (i=0; i<STYLES; i++) {
entry_style& ent = mEntryStyleArray.editItemAt(i);
const size_t N = ent.spans.size();
const size_t totalSize = (N*sizeof(ResStringPool_span))
+ sizeof(ResStringPool_ref);
ent.offset = styPos-strPos;
uint8_t* dat = (uint8_t*)pool->editData(preSize + styPos + totalSize);
if (dat == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: Out of memory for string styles\n");
return NO_MEMORY;
}
/* 字符串樣式在StringBlock中是組裝成一個ResStringPoll_span類型存儲起來 */
ResStringPool_span* span = (ResStringPool_span*)(dat+preSize+styPos);
for (size_t i=0; i<N; i++) {
span->name.index = htodl(ent.spans[i].span.name.index);
span->firstChar = htodl(ent.spans[i].span.firstChar);
span->lastChar = htodl(ent.spans[i].span.lastChar);
span++;
}
/* 寫入每個字符串樣式結尾符 */
span->name.index = htodl(ResStringPool_span::END);
styPos += totalSize;
}
/* 在StringBlock中寫入樣式結束符號 */
if (STYLES > 0) {
// Add full terminator at the end (when reading we validate that
// the end of the pool is fully terminated to simplify error
// checking).
size_t extra = sizeof(ResStringPool_span)-sizeof(ResStringPool_ref);
uint8_t* dat = (uint8_t*)pool->editData(preSize + styPos + extra);
if (dat == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: Out of memory for string styles\n");
return NO_MEMORY;
}
uint32_t* p = (uint32_t*)(dat+preSize+styPos);
while (extra > 0) {
*p++ = htodl(ResStringPool_span::END);
extra -= sizeof(uint32_t);
}
styPos += extra;
}
// Write header.
// 字符串緩沖區開始位置寫入一個記錄字符串緩沖區信息的ResStringPool_header
ResStringPool_header* header =
(ResStringPool_header*)pool->padData(sizeof(uint32_t));
if (header == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: Out of memory for string pool\n");
return NO_MEMORY;
}
memset(header, 0, sizeof(*header));
header->header.type = htods(RES_STRING_POOL_TYPE);
header->header.headerSize = htods(sizeof(*header));
header->header.size = htodl(pool->getSize());
header->stringCount = htodl(ENTRIES);
header->styleCount = htodl(STYLES);
if (mUTF8) {
header->flags |= htodl(ResStringPool_header::UTF8_FLAG);
}
header->stringsStart = htodl(preSize);
header->stylesStart = htodl(STYLES > 0 ? (preSize+strPos) : 0);
// Write string index array.
// 寫入字符串偏移數組
uint32_t* index = (uint32_t*)(header+1);
for (i=0; i<ENTRIES; i++) {
entry& ent = mEntries.editItemAt(mEntryArray[i]);
*index++ = htodl(ent.offset);
}
// Write style index array.
// 寫入字符串樣式偏移數組寫入
for (i=0; i<STYLES; i++) {
*index++ = htodl(mEntryStyleArray[i].offset);
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
至此,我們就將收集在StringPool中的xml文本文件的信息,按照指定組織方式以二進制的存儲方式存儲在一塊內存塊中,接下來我們繼續分析xml文本文件是如何被flatten的,其具體實現如下所示:
路徑:frameworks/base/tools/aapt/XMLNode.cpp
status_t XMLNode::flatten(const sp<AaptFile>& dest,
bool stripComments, bool stripRawValues) const
{
StringPool strings(mUTF8);
Vector<uint32_t> resids;
......
/* 收集到的屬性信息都保存在strings所指向的字符串資源池
** 現在為這些字符串資源池中的屬性信息分配字符串塊
*/
sp<AaptFile> stringPool = strings.createStringBlock();
/* 接著創建一個ResXMLTree_header */
ResXMLTree_header header;
memset(&header, 0, sizeof(header));
header.header.type = htods(RES_XML_TYPE);
header.header.headerSize = htods(sizeof(header));
const size_t basePos = dest->getSize();
/* 在匿名AdaptFile對象dest中先寫入一個header對象用於記錄信息,接著
** 將我們上面組織好的二進制xml字符串信息內存緩沖塊中數據寫入這個
** 匿名AdaptFile對象dest中的緩沖區去 */
dest->writeData(&header, sizeof(header));
dest->writeData(stringPool->getData(), stringPool->getSize());
// If we have resource IDs, write them.
// 如果已經分配了資源ID則先寫入一個記錄資源ID信息的ResChunk_header
// 頭,然後將資源ID的信息寫入,但是這裡尚未對任何資源分配資源ID.
if (resids.size() > 0) {
const size_t resIdsPos = dest->getSize();
const size_t resIdsSize =
sizeof(ResChunk_header)+(sizeof(uint32_t)*resids.size());
ResChunk_header* idsHeader = (ResChunk_header*)
(((const uint8_t*)dest->editData(resIdsPos+resIdsSize))+resIdsPos);
idsHeader->type = htods(RES_XML_RESOURCE_MAP_TYPE);
idsHeader->headerSize = htods(sizeof(*idsHeader));
idsHeader->size = htodl(resIdsSize);
uint32_t* ids = (uint32_t*)(idsHeader+1);
for (size_t i=0; i<resids.size(); i++) {
*ids++ = htodl(resids[i]);
}
}
/* 調用flatten_node函數繼續組織收集到的xml文件中的信息 */
flatten_node(strings, dest, stripComments, stripRawValues);
/* 最後,再寫入一個ResXMLTree_header標記寫入工作完成並記錄上次寫入這類
** header到剛剛創建的header之間寫入的數據信息
*/
void* data = dest->editData();
ResXMLTree_header* hd = (ResXMLTree_header*)(((uint8_t*)data)+basePos);
size_t size = dest->getSize()-basePos;
hd->header.size = htodl(dest->getSize()-basePos);
return NO_ERROR;
}
status_t XMLNode::flatten_node(const StringPool& strings, const sp<AaptFile>& dest,
bool stripComments, bool stripRawValues) const
{
ResXMLTree_node node;
ResXMLTree_cdataExt cdataExt;
ResXMLTree_namespaceExt namespaceExt;
ResXMLTree_attrExt attrExt;
const void* extData = NULL;
size_t extSize = 0;
ResXMLTree_attribute attr;
bool writeCurrentNode = true;
/* NA和NC分別記錄屬性個數和子標簽個數 */
const size_t NA = mAttributes.size();
const size_t NC = mChildren.size();
size_t i;
const String16 id16("id");
const String16 class16("class");
const String16 style16("style");
const type type = getType(); // 獲取當前處理的XMLNode所記錄信息的類型
/* 初始化一個node變量和attr變量 */
memset(&node, 0, sizeof(node));
memset(&attr, 0, sizeof(attr));
node.header.headerSize = htods(sizeof(node));
node.lineNumber = htodl(getStartLineNumber());
if (!stripComments) {
/* 返回注釋字符串在StringPool 的成員變量mValues中的位置 */
node.comment.index = htodl(
mComment.size() > 0 ? strings.offsetForString(mComment) : -1);
} else {
node.comment.index = htodl((uint32_t)-1);
}
if (type == TYPE_ELEMENT) {
/* 設置該node類型 */
node.header.type = htods(RES_XML_START_ELEMENT_TYPE);
/* 使用attrExt記錄一個attribute額外的信息 */
extData = &attrExt;
extSize = sizeof(attrExt);
memset(&attrExt, 0, sizeof(attrExt));
if (mNamespaceUri.size() > 0) {
attrExt.ns.index = htodl(strings.offsetForString(mNamespaceUri));
} else {
attrExt.ns.index = htodl((uint32_t)-1);
}
attrExt.name.index = htodl(strings.offsetForString(mElementName));
attrExt.attributeStart = htods(sizeof(attrExt));
attrExt.attributeSize = htods(sizeof(attr));
attrExt.attributeCount = htods(NA);
attrExt.idIndex = htods(0);
attrExt.classIndex = htods(0);
attrExt.styleIndex = htods(0);
for (i=0; i<NA; i++) {
ssize_t idx = mAttributeOrder.valueAt(i);
 Android動畫之屬性動畫(上)
Android動畫之屬性動畫(上)
前言在前面的文章中我們講述了Android動畫之視圖動畫學習了怎麼對一個view實現動畫,可以實現動畫包括平移,旋轉,縮放,漸變和幀動畫,這一篇我們來學習一個新的動畫實現
 Android學習之路之ListView的使用
Android學習之路之ListView的使用
學習android三天了,發現這個ListView在android裡應用非常的多,於是就花了一些時間仔細學習了一下! 以下是我個人的理解,如果有錯誤或不周到的地方,還請各
 Android手機鬧鐘用法實例
Android手機鬧鐘用法實例
本文實例講述了Android手機鬧鐘用法。分享給大家供大家參考。具體如下:一、開發手機鬧鐘主要用到了AlarmManager類,AlarmManager類提供了訪問系統定
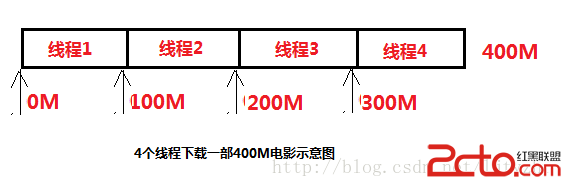 Android多線程下載大文件解析
Android多線程下載大文件解析
1、多線程介紹 用過迅雷的同學都知道,迅雷有個功能叫做多線程,還有一個叫離線下載,我們這裡重點介紹一下多線程下載。多線程,顧名思義就是很多歌線程同時在運行