編輯:關於Android編程
android手機的屏幕尺寸問題一直是讓開發者感覺很頭疼的問題,由於各手機廠商所采用的屏幕尺寸不同,user UI接口呈現及布局自然也各自迥異。所以,在開發android手機應用程序時,除了對底層API的掌握之外,最重要的仍是屏幕分辨率概念的理解。
android可設置為隨著窗口大小調整縮放比例,但即便如此,手機程序設計人員還是必須清楚地知道手機屏幕的邊界,以免縮放之後造成的布局(Layout)變形問題。在android中,只需幾行代碼就可以取得手機屏幕分辨率,其中的關鍵則是DisplayMetrics類的應用。
DisplayMetrics類直接繼承自Object類,存放在Android.util包下。DisplayMetrics對象記錄了一些常用的信息,包含了顯示信息、大小、維度和字體等,如下表所示:
static int DEFAULT_DENSITY
The reference density used throughout the system.
float density
The logical density of the display.
int heightPixels
The absolute height of the display in pixels.
float scaledDensity
A scaling factor for fonts displayed on the display.
int widthPixels
The absolute width of the display in pixels.
float xdpi
The exact physical pixels per inch of the screen in the X dimension.
float ydpi
The exact physical pixels per inch of the screen in the Y dimension.
值得一提的是,widthPixels和heightPixels記錄了手機屏幕的寬和高,我們使用這兩個值便可得到手機屏幕分辨率。注意此處的像素指的是絕對(Absolute)像素,而非相對像素。
下面是獲取屏幕分辨率的代碼:
[java] public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
private TextView text=null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
this.text=(TextView)super.findViewById(R.id.text);
DisplayMetrics dm=new DisplayMetrics();
super.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(dm);
String strOpt="手機屏幕分辨率為:"+dm.widthPixels+"*"+dm.heightPixels;
this.text.setText(strOpt);
}
}
public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
private TextView text=null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
this.text=(TextView)super.findViewById(R.id.text);
DisplayMetrics dm=new DisplayMetrics();
super.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(dm);
String strOpt="手機屏幕分辨率為:"+dm.widthPixels+"*"+dm.heightPixels;
this.text.setText(strOpt);
}
}
布局文件非常簡單,一個TextView組件即可:
[html] <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</RelativeLayout>
程序運行效果截圖:
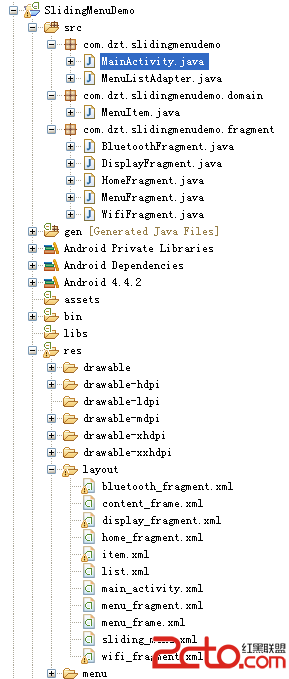 Android開源項目SlidingMenu的學習筆記(二)
Android開源項目SlidingMenu的學習筆記(二)
在前面已經介紹了SlidingMenu的用法:Android開源項目SlidingMenu的學習筆記(一),接下來再深入學習下,根據滑出項的Menu切換到對應的頁面 目錄
 php使用phpmailer發送郵件實例解析
php使用phpmailer發送郵件實例解析
本人新手,由於要做郵件發送驗證碼,所以找到和搜集到這些,本人親測完全可以用這是163郵箱的 因為不是企業郵箱填寫的賬號是163的賬號,但是密碼是授
 android launchmode 使用場景
android launchmode 使用場景
菜鳥起飛記android launchmode 使用場景Activity一共有以下四種launchMode:1.standard2.singleTop3.singleTa
 Android開發之使用HTTP訪問網絡資源
Android開發之使用HTTP訪問網絡資源
使用HTTP訪問網絡資源 前面介紹了 URLConnection己經可以非常方便地與指定站點交換信息,URLConnection還有一個子類:HttpURL