編輯:關於Android編程
Android SDK集成了Apache HttpClient模塊。要注意的是,這裡的Apache HttpClient模塊是HttpClient 4.0(org.apache.http.*),而不是常見的 Jakarta Commons HttpClient 3.x(org.apache.commons.httpclient.*)。
HttpClient常用HttpGet和HttpPost這兩個類,分別對應Get方式和Post方式。
無論是使用HttpGet,還是使用HttpPost,都必須通過如下3步來訪問HTTP資源。
1.創建HttpGet或HttpPost對象,將要請求的URL通過構造方法傳入HttpGet或HttpPost對象。
2.使用DefaultHttpClient類的execute方法發送HTTP GET或HTTP POST請求,並返回HttpResponse對象。
3.通過HttpResponse接口的getEntity方法返回響應信息,並進行相應的處理。
如果使用HttpPost方法提交HTTP POST請求,則需要使用HttpPost類的setEntity方法設置請求參數。參數則必須用NameValuePair[]數組存儲。
下面給出一些實例:
Get方式:
[java] // HttpGet方式請求
public static void requestByHttpGet() throws Exception {
String path = "https://reg.163.com/logins.jsp?id=helloworld&pwd=android";
// 新建HttpGet對象
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(path);
// 獲取HttpClient對象
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
// 獲取HttpResponse實例
HttpResponse httpResp = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// 判斷是夠請求成功
if (httpResp.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HTTP_200) {
// 獲取返回的數據
String result = EntityUtils.toString(httpResp.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
Log.i(TAG_HTTPGET, "HttpGet方式請求成功,返回數據如下:");
Log.i(TAG_HTTPGET, result);
} else {
Log.i(TAG_HTTPGET, "HttpGet方式請求失敗");
}
}
// HttpGet方式請求
public static void requestByHttpGet() throws Exception {
String path = "https://reg.163.com/logins.jsp?id=helloworld&pwd=android";
// 新建HttpGet對象
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(path);
// 獲取HttpClient對象
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
// 獲取HttpResponse實例
HttpResponse httpResp = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// 判斷是夠請求成功
if (httpResp.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HTTP_200) {
// 獲取返回的數據
String result = EntityUtils.toString(httpResp.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
Log.i(TAG_HTTPGET, "HttpGet方式請求成功,返回數據如下:");
Log.i(TAG_HTTPGET, result);
} else {
Log.i(TAG_HTTPGET, "HttpGet方式請求失敗");
}
}
[java] public String doGet()
{
String uriAPI = "http://XXXXX?str=I+am+get+String";
String result= "";
// HttpGet httpRequst = new HttpGet(URI uri);
// HttpGet httpRequst = new HttpGet(String uri);
// 創建HttpGet或HttpPost對象,將要請求的URL通過構造方法傳入HttpGet或HttpPost對象。
HttpGet httpRequst = new HttpGet(uriAPI);
// new DefaultHttpClient().execute(HttpUriRequst requst);
try {
//使用DefaultHttpClient類的execute方法發送HTTP GET請求,並返回HttpResponse對象。
HttpResponse httpResponse = new DefaultHttpClient().execute(httpRequst);//其中HttpGet是HttpUriRequst的子類
if(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200)
{
HttpEntity httpEntity = httpResponse.getEntity();
result = EntityUtils.toString(httpEntity);//取出應答字符串
// 一般來說都要刪除多余的字符
result.replaceAll("\r", "");//去掉返回結果中的"\r"字符,否則會在結果字符串後面顯示一個小方格
}
else
httpRequst.abort();
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
result = e.getMessage().toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
result = e.getMessage().toString();
}
return result;
}
public String doGet()
{
String uriAPI = "http://XXXXX?str=I+am+get+String";
String result= "";
// HttpGet httpRequst = new HttpGet(URI uri);
// HttpGet httpRequst = new HttpGet(String uri);
// 創建HttpGet或HttpPost對象,將要請求的URL通過構造方法傳入HttpGet或HttpPost對象。
HttpGet httpRequst = new HttpGet(uriAPI);
// new DefaultHttpClient().execute(HttpUriRequst requst);
try {
//使用DefaultHttpClient類的execute方法發送HTTP GET請求,並返回HttpResponse對象。
HttpResponse httpResponse = new DefaultHttpClient().execute(httpRequst);//其中HttpGet是HttpUriRequst的子類
if(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200)
{
HttpEntity httpEntity = httpResponse.getEntity();
result = EntityUtils.toString(httpEntity);//取出應答字符串
// 一般來說都要刪除多余的字符
result.replaceAll("\r", "");//去掉返回結果中的"\r"字符,否則會在結果字符串後面顯示一個小方格
}
else
httpRequst.abort();
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
result = e.getMessage().toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
result = e.getMessage().toString();
}
return result;
}
Post方式:
如果使用HttpPost方法提交HTTP POST請求,則需要使用HttpPost類的setEntity方法設置請求參數。參數則必須用NameValuePair[]數組存儲。
[java] <STRONG>public String doPost()
{
String uriAPI = "http://XXXXXX";//Post方式沒有參數在這裡
String result = "";
HttpPost httpRequst = new HttpPost(uriAPI);//創建HttpPost對象
List <NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("str", "I am Post String"));
try {
httpRequst.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(params,HTTP.UTF_8));
HttpResponse httpResponse = new DefaultHttpClient().execute(httpRequst);
if(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200)
{
HttpEntity httpEntity = httpResponse.getEntity();
result = EntityUtils.toString(httpEntity);//取出應答字符串
}
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
result = e.getMessage().toString();
}
catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
result = e.getMessage().toString();
}
catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
result = e.getMessage().toString();
}
return result;
} </STRONG>
public String doPost()
{
String uriAPI = "http://XXXXXX";//Post方式沒有參數在這裡
String result = "";
HttpPost httpRequst = new HttpPost(uriAPI);//創建HttpPost對象
List <NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("str", "I am Post String"));
try {
httpRequst.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(params,HTTP.UTF_8));
HttpResponse httpResponse = new DefaultHttpClient().execute(httpRequst);
if(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200)
{
HttpEntity httpEntity = httpResponse.getEntity();
result = EntityUtils.toString(httpEntity);//取出應答字符串
}
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
result = e.getMessage().toString();
}
catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
result = e.getMessage().toString();
}
catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
result = e.getMessage().toString();
}
return result;
}
[java] <STRONG>// HttpPost方式請求
public static void requestByHttpPost() throws Exception {
String path = "https://reg.163.com/logins.jsp";
// 新建HttpPost對象
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(path);
// Post參數
List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("id", "helloworld"));
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("pwd", "android"));
// 設置字符集
HttpEntity entity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(params, HTTP.UTF_8);
// 設置參數實體
httpPost.setEntity(entity);
// 獲取HttpClient對象
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
// 獲取HttpResponse實例
HttpResponse httpResp = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
// 判斷是夠請求成功
if (httpResp.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HTTP_200) {
// 獲取返回的數據
String result = EntityUtils.toString(httpResp.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
Log.i(TAG_HTTPGET, "HttpPost方式請求成功,返回數據如下:");
Log.i(TAG_HTTPGET, result);
} else {
Log.i(TAG_HTTPGET, "HttpPost方式請求失敗");
}
} </STRONG>
 Android ListView組件詳解及示例代碼
Android ListView組件詳解及示例代碼
Android 列表組件 ListView列表組件是開發中經常用到組件,使用該組件在使用時需要為它提供適配器,由適配器提供來確定顯示樣式和顯示數據。下面看一個例子:新建一
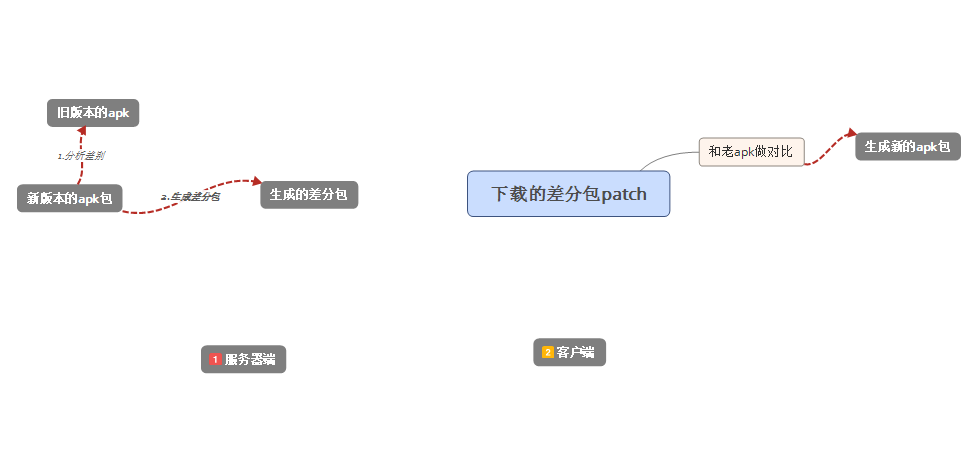 Android的增量更新,差分更新--服務器端&客戶端
Android的增量更新,差分更新--服務器端&客戶端
前言隨著應用越來越大,應用更新耗時間和流量的問題,就顯得格外突出.目前原生app的更新分為兩種:重新下載源文件,還有一種就是差分包更新,也叫增量更新.在有些應用市場,例如
 Android AsyncTask使用以及源碼解析
Android AsyncTask使用以及源碼解析
綜述 在Android中,我們需要進行一些耗時的操作,會將這個操作放在子線程中進行。在子線程操作完成以後我們可以通過Handler進行發送消息,通知UI進行一些更新操作
 Android之斷點續傳下載
Android之斷點續傳下載
今天學習了Android開發中比較難的一個環節,就是斷點續傳下載,很多人看到這個標題就感覺頭大,的確,如果沒有良好的邏輯思維,這塊的確很難搞明白。下面我就將自己學到的知