編輯:關於Android編程
Android中ListView的用法,原文如下:
ListView是一個經常用到的控件,ListView裡面的每個子項Item可以使一個字符串,也可以是一個組合控件。先說說ListView的實現:
1.准備ListView要顯示的數據 ;
2.使用 一維或多維 動態數組 保存數據;
2.構建適配器 , 簡單地來說, 適配器就是 Item數組 , 動態數組 有多少元素就生成多少個Item;
3.把 適配器 添加到ListView,並顯示出來。
接下來,看看本文代碼所實現的ListView:
接下來,就開始UI的XML代碼:
main.xml代碼如下,很簡單,也不需要多做解釋了:
[plain]
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/LinearLayout01"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<ListViewandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/MyListView">
</ListView>
</LinearLayout>
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/LinearLayout01"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<ListViewandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/MyListView">
</ListView>
</LinearLayout>
布局文件:my_listitem.xml的代碼如下,my_listitem.xml用於設計ListView的Item:
[html]
<?xmlversionxmlversion="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/MyListItem"
android:paddingBottom="3dip"
android:paddingLeft="10dip">
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:id="@+id/ItemTitle"
android:textSize="30dip">
</TextView>
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:id="@+id/ItemText">
</TextView>
</LinearLayout>
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/MyListItem"
android:paddingBottom="3dip"
android:paddingLeft="10dip">
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:id="@+id/ItemTitle"
android:textSize="30dip">
</TextView>
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:id="@+id/ItemText">
</TextView>
</LinearLayout>
解釋一下,裡面用到的一些屬性:
1.paddingBottom="3dip",Layout往底部留出3個像素的空白區域
2.paddingLeft="10dip",Layout往左邊留出10個像素的空白區域
3.textSize="30dip",TextView的字體為30個像素那麼大。
最後就是JAVA的源代碼:
[javascript]
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//綁定XML中的ListView,作為Item的容器
ListView list = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.MyListView);
//生成動態數組,並且轉載數據
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> mylist =new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>();
for(inti=0;i<30;i++)
{
HashMap<String, String> map = newHashMap<String, String>();
map.put("ItemTitle","This is Title.....");
map.put("ItemText","This is text.....");
mylist.add(map);
}
//生成適配器,數組===》ListItem
SimpleAdapter mSchedule =new SimpleAdapter(this,//沒什麼解釋
mylist,//數據來源
R.layout.my_listitem,//ListItem的XML實現
//動態數組與ListItem對應的子項
new String[] {"ItemTitle","ItemText"},
//ListItem的XML文件裡面的兩個TextView ID
new int[] {R.id.ItemTitle,R.id.ItemText});
//添加並且顯示
list.setAdapter(mSchedule);
}
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//綁定XML中的ListView,作為Item的容器
ListView list = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.MyListView);
//生成動態數組,並且轉載數據
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> mylist =new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>();
for(inti=0;i<30;i++)
{
HashMap<String, String> map = newHashMap<String, String>();
map.put("ItemTitle","This is Title.....");
map.put("ItemText","This is text.....");
mylist.add(map);
}
//生成適配器,數組===》ListItem
SimpleAdapter mSchedule =new SimpleAdapter(this,//沒什麼解釋
mylist,//數據來源
R.layout.my_listitem,//ListItem的XML實現
//動態數組與ListItem對應的子項
new String[] {"ItemTitle","ItemText"},
//ListItem的XML文件裡面的兩個TextView ID
new int[] {R.id.ItemTitle,R.id.ItemText});
//添加並且顯示
list.setAdapter(mSchedule);
}
//數據庫獲取數據
[java]
DBHelper helper=new DBHelper(this);
Cursor c=helper.query();
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> mylist = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>();
int i=0;
while (c.moveToNext()) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("title",c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("Title")));
map.put("date",c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("Date")));
mylist.add(map);
i++;
}
String[] from={"title","date"};
int[] to={R.id.ItemTitle,R.id.ItemDate};
SimpleAdapter ada=new SimpleAdapter(this,mylist,R.layout.listitem,from,to);
ListView list = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.MyListView);
list.setAdapter(ada);
DBHelper helper=new DBHelper(this);
Cursor c=helper.query();
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> mylist = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>();
int i=0;
while (c.moveToNext()) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("title",c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("Title")));
map.put("date",c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("Date")));
mylist.add(map);
i++;
}
String[] from={"title","date"};
int[] to={R.id.ItemTitle,R.id.ItemDate};
SimpleAdapter ada=new SimpleAdapter(this,mylist,R.layout.listitem,from,to);
ListView list = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.MyListView);
list.setAdapter(ada);
 Android編程基於Contacts讀取聯系人的方法(附demo源碼)
Android編程基於Contacts讀取聯系人的方法(附demo源碼)
本文實例講述了Android編程基於Contacts讀取聯系人的方法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:Android Contacts簡介:這裡介紹安卓通訊錄數據庫。包括
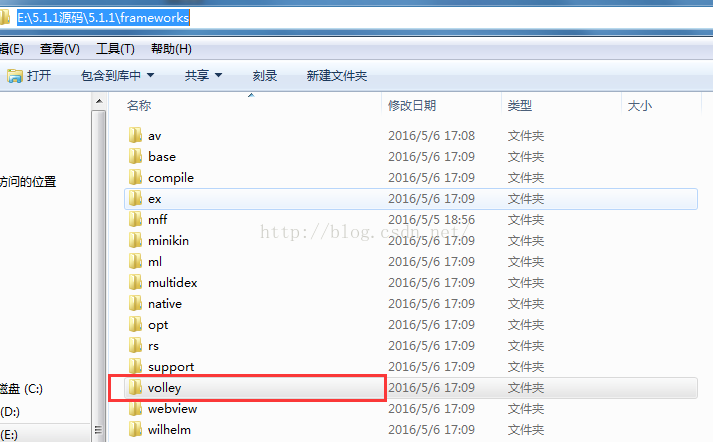 Android Volley小白解析(一)
Android Volley小白解析(一)
做安卓一年有余,意識到網絡請求框架算是很重要的一塊,考慮到Volley是谷歌自帶的,決定好好研究研究源碼,去理理邏輯思路首先呢,Volley去哪裡獲取,看下圖即可,在安卓
 Android簡易實戰教程--第二十四話《畫畫板》
Android簡易實戰教程--第二十四話《畫畫板》
今天完成一個畫畫板。首先來個布局: 可見,要分紅綠色,而且還要保存最後畫的圖片。 看一下主活動代碼: package com.it
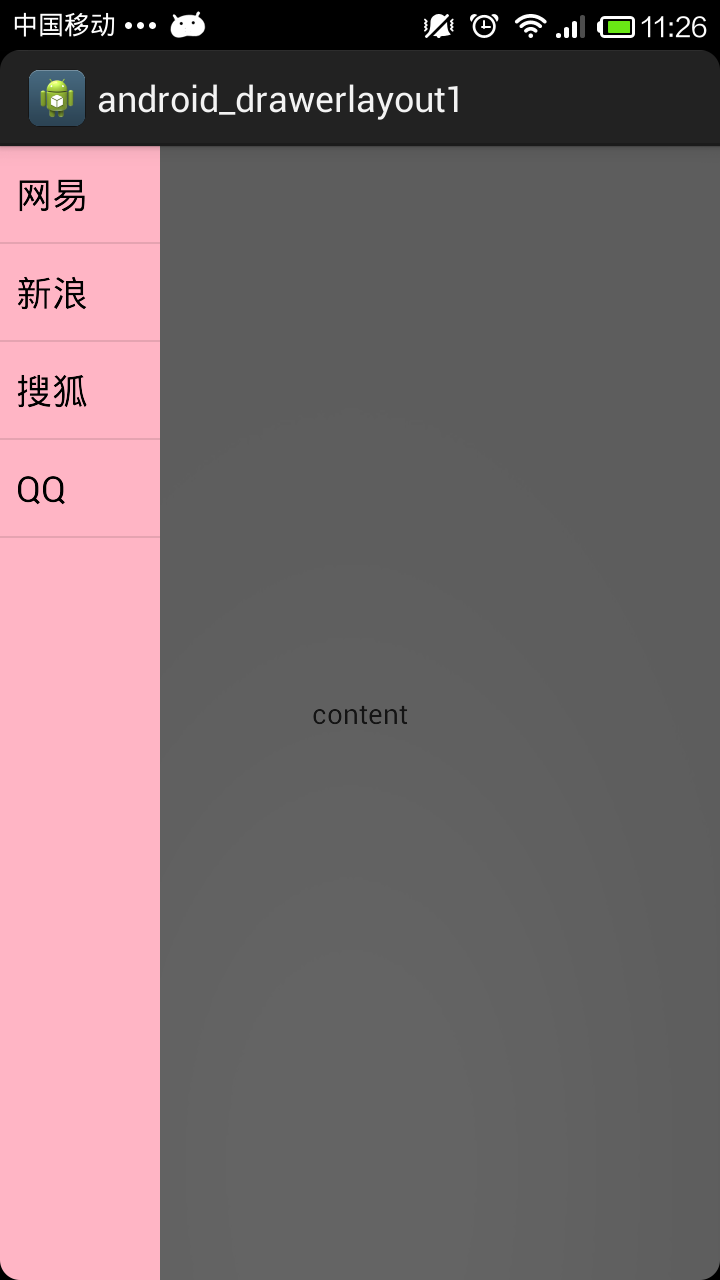 使用DrawerLayout組件實現側滑抽屜的功能
使用DrawerLayout組件實現側滑抽屜的功能
DrawerLayout組件同樣是V4包中的組件,也是直接繼承於ViewGroup類,所以這個類也是一個容器類。使用DrawerLayout可以輕松的實現抽屜效果,使用D