1.Camera架構包括客戶端和服務端,他們之間的通信采用Binder機制實現。
Camera的實現主要包括本地代碼和Java代碼兩個層次:
Camera本地框架:
frameworks/native/include/ui
frameworks/native/libs/ui
frameworks/av/camera/
Camera的本地實現包含在上述目錄中,這部分內容被編譯生成庫libui.so和libcamera_client.so。
Camera服務部分:
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice
這部分編譯生成libcameraservice.so。
Camera HAL:
frameworks/av/camera
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/CameraHardwareInterface.h
CameraHardwareInterface.h是HAL接口的定義,需要各個系統根據自己的情況實現。
2.AndroidCamera采用C/S架構,client與server兩個獨立的線程之間使用Binder通信。這裡將介紹Camera從設備開機,到進入相機應用是如何完成初始化工作的。
首先既然Camera是利用binder通信,它肯定要將它的service注冊到ServiceManager裡面,以備後續Client引用,那麼這一步是在哪裡進行的呢?在frameworks/av/media/mediaserver/main_mediaserver.cpp下有個main函數,可以用來注冊媒體服務。在這裡,CameraService完成了服務的注冊。
intmain(int argc, char** argv)
{
sp<ProcessState>proc(ProcessState::self());
sp<IServiceManager> sm= defaultServiceManager();
ALOGI("ServiceManager:%p", sm.get());
AudioFlinger::instantiate();
MediaPlayerService::instantiate();
CameraService::instantiate();
AudioPolicyService::instantiate();
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
}
可是我們到CameraService文件裡面卻找不到instantiate()這個函數,它在哪?繼續追到它的一個父類BinderService
template<typenameSERVICE>
classBinderService
{
public:
static status_t publish(bool allowIsolated =false) {
sp<IServiceManager>sm(defaultServiceManager());
returnsm->addService(String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()), new SERVICE(),allowIsolated);
}
static void publishAndJoinThreadPool(boolallowIsolated = false) {
sp<IServiceManager>sm(defaultServiceManager());
sm->addService(String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()),new SERVICE(), allowIsolated);
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
}
staticvoid instantiate(){ publish(); }
static status_t shutdown() {
return NO_ERROR;
}
};
可以發現在publish()函數中,CameraService完成服務的注冊。這裡面有個SERVICE,源碼中有說明
template<typenameSERVICE>
這表示SERVICE是個模板,這裡是注冊CameraService,所以可以用CameraService代替
sm->addService(String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()),new SERVICE(), allowIsolated);
這樣,Camera就在ServiceManager完成服務注冊,提供給client隨時使用。
Main_MediaServer主函數由init.rc在啟動是調用,所以在設備開機的時候Camera就會注冊一個服務,用作binder通信。
servicemedia /system/bin/mediaserver
class main
user media
group audio camera inetnet_bt net_bt_admin net_bw_acct drmrpc
ioprio rt 4
Binder服務已注冊,那接下來就看看client如何連上server端,並打開camera模塊。
咱們先從testingcameraapp的源碼入手。在setUpCamera()函數中專門有一個open(mCameraId)函數進入framework層,調用frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/Camera.java類的open方法。
publicstatic Camera open(int cameraId) {
return newCamera(cameraId);
}
這裡調用了Camera的構造函數,在看看構造函數
Camera(int cameraId) {
mShutterCallback = null;
mRawImageCallback = null;
mJpegCallback = null;
mPreviewCallback = null;
mPostviewCallback = null;
mZoomListener = null;
Looper looper;
if ((looper =Looper.myLooper()) != null) {
mEventHandler = newEventHandler(this, looper);
} else if ((looper =Looper.getMainLooper()) != null) {
mEventHandler = newEventHandler(this, looper);
} else {
mEventHandler = null;
}
native_setup(newWeakReference<Camera>(this), cameraId);
}
好,終於來到JNI了,繼續看camera的JNI文件frameworks/base/core/jni/android_hardware_Camera.cpp
// connect to cameraservice
static voidandroid_hardware_Camera_native_setup(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz,
jobject weak_this,jint cameraId)
{
sp<Camera>camera = Camera::connect(cameraId);
if (camera == NULL) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env,"Fail to connect to camera service");
return;
}
// make sure camerahardware is alive
if(camera->getStatus() != NO_ERROR) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env,"Camera initialization failed");
return;
}
jclass clazz =env->GetObjectClass(thiz);
if (clazz == NULL) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env,"Can't find android/hardware/Camera");
return;
}
// We use a weakreference so the Camera object can be garbage collected.
// The reference isonly used as a proxy for callbacks.
sp<JNICameraContext>context = new JNICameraContext(env, weak_this, clazz, camera);
context->incStrong(thiz);
camera->setListener(context);
// save context inopaque field
env->SetIntField(thiz,fields.context, (int)context.get());
}
JNI函數裡面,我們找到CameraC/S架構的客戶端了,它調用connect函數向服務器發送連接請求。JNICameraContext這個類是一個監聽類,用於處理底層Camera回調函數傳來的數據和消息
看看客戶端的connect函數有什麼
===>>>frameworks/av/camera/Camera.cpp
sp<Camera>Camera::connect(int cameraId)
{
ALOGV("connect");
sp<Camera> c = new Camera();
const sp<ICameraService>& cs =getCameraService();
if (cs != 0) {
c->mCamera = cs->connect(c,cameraId);
}
if (c->mCamera != 0) {
c->mCamera->asBinder()->linkToDeath(c);
c->mStatus = NO_ERROR;
} else {
c.clear();
}
return c;
}
constsp<ICameraService>& cs =getCameraService();通過getCameraService()函數獲取一個Camera服務實例。
// establish binder interface to cameraservice
const sp<ICameraService>&Camera::getCameraService()
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
if (mCameraService.get() == 0) {
sp<IServiceManager> sm =defaultServiceManager();
sp<IBinder> binder;
do {
binder =sm->getService(String16("media.camera"));
if (binder != 0)
break;
ALOGW("CameraServicenot published, waiting...");
usleep(500000); // 0.5 s
} while(true);
if (mDeathNotifier == NULL) {
mDeathNotifier = newDeathNotifier();
}
binder->linkToDeath(mDeathNotifier);
mCameraService= interface_cast<ICameraService>(binder);
}
ALOGE_IF(mCameraService==0, "noCameraService!?");
return mCameraService;
}
可以看出,該CameraService實例是通過binder獲取的,由binder機制可以知道,該服務就是CameraService一個實例。
c->mCamera= cs->connect(c, cameraId);
然後執行服務端的connect()函數,並返回一個ICamera對象賦值給Camera的mCamera,服務端connect()返回的其實是它內部類client的一個實例。
sp<ICamera>CameraService::connect(
const sp<ICameraClient>&cameraClient, int cameraId) {
int callingPid = getCallingPid();
LOG1("CameraService::connect E(pid %d, id %d)", callingPid, cameraId);
if(!mModule) {
ALOGE("Camera HAL module not loaded");
return NULL;
}
sp<Client> client;
if (cameraId < 0 || cameraId >=mNumberOfCameras) {
ALOGE("CameraService::connectX (pid %d) rejected (invalid cameraId %d).",
callingPid, cameraId);
return NULL;
}
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("sys.secpolicy.camera.disabled", value, "0");
if (strcmp(value, "1") ==0) {
// Camera is disabled byDevicePolicyManager.
ALOGI("Camera is disabled.connect X (pid %d) rejected", callingPid);
return NULL;
}
Mutex::Autolock lock(mServiceLock);
if (mClient[cameraId] != 0) {
client =mClient[cameraId].promote();
if (client != 0) {
if(cameraClient->asBinder() ==client->getCameraClient()->asBinder()) {
LOG1("CameraService::connect X (pid %d) (the same client)",
callingPid);
return client;
} else {
ALOGW("CameraService::connect X (pid %d) rejected (existingclient).",
callingPid);
return NULL;
}
}
mClient[cameraId].clear();
}
if (mBusy[cameraId]) {
ALOGW("CameraService::connectX (pid %d) rejected"
" (camera %d isstill busy).", callingPid, cameraId);
return NULL;
}
struct camera_info info;
if(mModule->get_camera_info(cameraId, &info) != OK) {
ALOGE("Invalid camera id%d", cameraId);
return NULL;
}
int deviceVersion;
if(mModule->common.module_api_version ==CAMERA_MODULE_API_VERSION_2_0) {
deviceVersion =info.device_version;
} else {
deviceVersion =CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0;
}
switch(deviceVersion) {
caseCAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0:
client = new CameraClient(this,cameraClient, cameraId,
info.facing,callingPid, getpid());
break;
caseCAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_2_0:
client = newCamera2Client(this, cameraClient, cameraId,
info.facing,callingPid, getpid());
break;
default:
ALOGE("Unknown cameradevice HAL version: %d", deviceVersion);
return NULL;
}
if(client->initialize(mModule) != OK) {
return NULL;
}
cameraClient->asBinder()->linkToDeath(this);
mClient[cameraId] = client;
LOG1("CameraService::connect X(id %d, this pid is %d)", cameraId, getpid());
return client;
}
在函數client->initialize(mModule)中實例化CameraHal接口hardware,hardware調用initialize()進入HAL層打開Camear驅動
status_tCameraClient::initialize(camera_module_t *module) {
int callingPid = getCallingPid();
LOG1("CameraClient::initialize E (pid %d, id %d)",callingPid, mCameraId);
char camera_device_name[10];
status_t res;
snprintf(camera_device_name, sizeof(camera_device_name), "%d",mCameraId);
mHardware= new CameraHardwareInterface(camera_device_name);
res =mHardware->initialize(&module->common);
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: Camera %d: unable to initialize device: %s(%d)",
__FUNCTION__, mCameraId, strerror(-res), res);
mHardware.clear();
return NO_INIT;
}
mHardware->setCallbacks(notifyCallback,
dataCallback,
dataCallbackTimestamp,
(void *)mCameraId);
// Enable zoom, error, focus, and metadata messages by default
enableMsgType(CAMERA_MSG_ERROR | CAMERA_MSG_ZOOM |CAMERA_MSG_FOCUS |
CAMERA_MSG_PREVIEW_METADATA |CAMERA_MSG_FOCUS_MOVE);
LOG1("CameraClient::initialize X (pid %d, id %d)",callingPid, mCameraId);
return OK;
}
hardware調用initialize()進入HAL層打開Camear驅動
status_t initialize(hw_module_t *module)
{
ALOGI("Opening camera %s", mName.string());
int rc = module->methods->open(module, mName.string(),
(hw_device_t**)&mDevice); //這一句作用就是打開Camera底層驅動
if (rc != OK) {
ALOGE("Could not open camera %s: %d",mName.string(), rc);
return rc;
}
initHalPreviewWindow();
return rc;
}
hardware->initialize(&mModule->common)中mModule模塊是一個結構體camera_module_t,他是怎麼初始化的呢?我們發現CameraService裡面有個函數
voidCameraService::onFirstRef()
{
BnCameraService::onFirstRef();
if (hw_get_module(CAMERA_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
(const hw_module_t **)&mModule) < 0) {
ALOGE("Could not load camera HAL module");
mNumberOfCameras = 0;
}
else {
mNumberOfCameras = mModule->get_number_of_cameras();
if (mNumberOfCameras > MAX_CAMERAS) {
ALOGE("Number of cameras(%d) > MAX_CAMERAS(%d).",
mNumberOfCameras, MAX_CAMERAS);
mNumberOfCameras = MAX_CAMERAS;
}
for (int i = 0; i < mNumberOfCameras; i++) {
setCameraFree(i);
}
}
}
CameraService調用
hw_get_module(CAMERA_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,(const hw_module_t **)&mModule)
來裝載fakecamera HAL module:camera.duck.so
inthw_get_module(const char *id, const struct hw_module_t **module)
{
returnhw_get_module_by_class(id, NULL, module);
}
inthw_get_module_by_class(const char *class_id, const char *inst,
const struct hw_module_t **module)
{
int status;
int i;
const structhw_module_t *hmi = NULL;
charprop[PATH_MAX];
charpath[PATH_MAX];
charname[PATH_MAX];
if (inst)
snprintf(name, PATH_MAX, "%s.%s", class_id, inst);
else
strlcpy(name, class_id, PATH_MAX);
/*
* Here werely on the fact that calling dlopen multiple times on
* the same.so will simply increment a refcount (and not load
* a new copyof the library).
* We alsoassume that dlopen() is thread-safe.
*/
/* Loopthrough the configuration variants looking for a module */
for (i=0 ;i<HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT+1 ; i++) {
if (i <HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT) {
if(property_get(variant_keys[i], prop, NULL) == 0) {
continue;
}
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.%s.so",
HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2, name, prop);
if(access(path, R_OK) == 0) break;
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.%s.so",
HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1, name, prop);
if(access(path, R_OK) == 0) break;
} else {
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.default.so",
HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1, name);
if(access(path, R_OK) == 0) break;
}
}
camera.duck.somodule 的代碼在development/tools/emulator/system/camera/
====>development/tools/emulator/system/camera/Android.mk
LOCAL_SRC_FILES :=\
EmulatedCameraHal.cpp \
EmulatedCameraFactory.cpp \
EmulatedBaseCamera.cpp \
EmulatedCamera.cpp \
EmulatedCameraDevice.cpp \
EmulatedQemuCamera.cpp \
EmulatedQemuCameraDevice.cpp \
EmulatedFakeCamera.cpp \
EmulatedFakeCameraDevice.cpp \
Converters.cpp \
PreviewWindow.cpp \
CallbackNotifier.cpp \
QemuClient.cpp \
JpegCompressor.cpp \
EmulatedCamera2.cpp \
EmulatedFakeCamera2.cpp \
EmulatedQemuCamera2.cpp \
fake-pipeline2/Scene.cpp \
fake-pipeline2/Sensor.cpp \
fake-pipeline2/JpegCompressor.cpp
ifeq($(TARGET_PRODUCT),vbox_x86)
LOCAL_MODULE :=camera.vbox_x86
else
LOCAL_MODULE :=camera.duck
endif
了解HAL層的都知道hw_get_module函數就是用來獲取模塊的Halstub,這裡是通過CAMERA_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID獲取CameraHal層的代理stub,並賦值給mModule,後面就可通過操作mModule完成對Camera模塊的控制。那麼onFirstRef()函數又是何時調用的?
onFirstRef()屬於其父類RefBase,該函數在強引用sp新增引用計數時調用,什麼意思?就是當有sp包裝的類初始化的時候調用,那麼camera是何時調用的呢?可以發現在
客戶端發起連接時候
sp<Camera>Camera::connect(int cameraId)
{
LOGV("connect");
sp<Camera> c = new Camera();
constsp<ICameraService>& cs = getCameraService();
}
這個時候初始化了一個CameraService實例,且用Sp包裝,這個時候sp將新增計數,相應的CameraService實例裡面onFirstRef()函數完成調用。
CameraService::connect()返回client的時候,就表明客戶端和服務端連接建立。Camera完成初始化,可以進行拍照和preview等動作。
 實現360手機助手TabHost的波紋效果
實現360手機助手TabHost的波紋效果
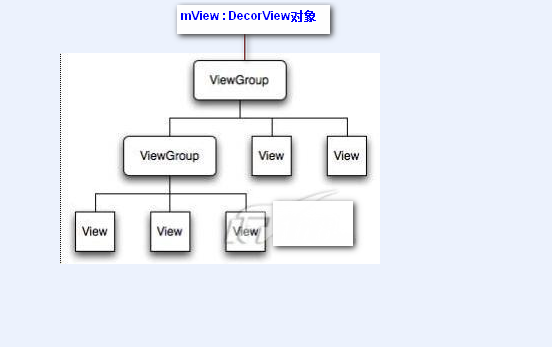 自定義控件_day01
自定義控件_day01
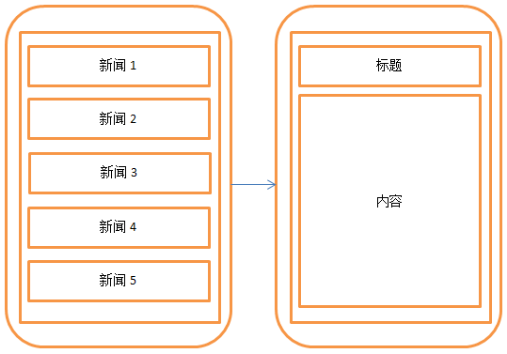 Fragment(碎片)(1)
Fragment(碎片)(1)
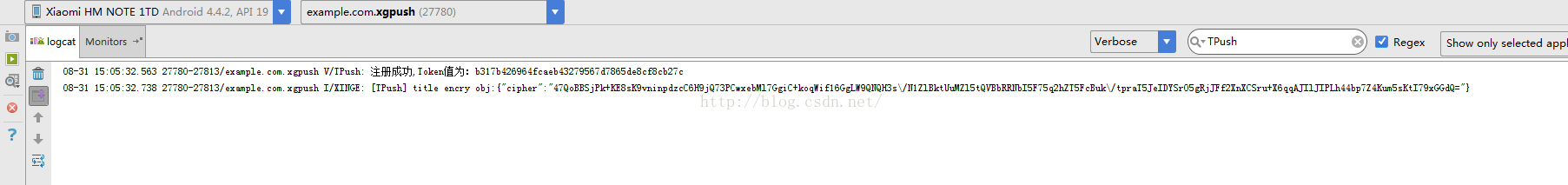 Android項目集成信鴿推送過程詳解
Android項目集成信鴿推送過程詳解