編輯:關於Android編程
每一個android應用程序都在他自己的進程中運行,都有一個獨立的Dalvik虛擬機實例,防止虛擬器崩潰時所有的chengx。Dalvik虛擬機是基於寄存器的,JVM是基於棧的。
應用解析:
1.Activity:用戶所能看到的屏幕,用來處理應用的整體性工作。如監聽系統事件、為用戶顯示指定的View、啟動其他的activity等。
2.Intent:實現activity之間的切換。Intent描述應用想做什麼,是應用程序的意圖。Intent數據結構包括動作和動作所對應的數據。動作對應的數據用URI來進行表示。與之對應的是一個intentfilter,描述activity或intentreceiver能夠操作那些intent,intentfilter要知道怎麼去處理動作和URI,需要在AndroidManifest.xml中聲明。調用startActivity(intent)實現activity的切換。重復利用intent,產生新的activity。
Intent showNextPage_intent = new Intent();
showNextPage_intent.setClass(this,NextPageActivity.class);
startActivity(showNextPage_intent);
3.IntentReceiver:對外部的事件進行響應,可以在AndroidManifest.xml和Context.registerReceiver()中注冊。
4.Service:具有生命周期的一種服務。使用Context.startService()來啟動一個service,並在後台運行該服務。Context.bindService()綁定到一個service上,通過service提供的接口與他進行通信,比如播放器的暫停,重播等操作。
生命周期:1>startService開始,stopService結束。
2>與bindService進程同生共死,或者調用unbindService結束。
3>混合使用需要stopservice和unbindService都結束,Service終止。
使用服務:Context.startService();Context.bindService()兩種方式。
//音樂播放器的service實例//Manifest.xml中的Service定義
<service android:name=".Music">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.liangshan.wuyong.START_AUDIO_SERVICE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.default" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
//Service子類中的Player
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
super.onStart(intent, startId);
player = MediaPlayer.create(this, R.raw.seven_days);
player.start();
}
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
player.stop();
}
//Activity 中定義的Intent開啟相應的Service
startService(new Intent("com.gruden.sy.START_AUDIO_SERVICE"));
stopService(new Intent("com.gruden.sy.START_AUDIO_SERVICE"));
5.ContentProvider:數據共享,針對不同應用包或程序之間實現數據共享的解決方案。
6.Bundle:使用Bundle在activity之間傳輸數據,和activity及Intent聯系較為密切。
//數據寫入Intent
Intent intent = new Intent();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("key_Name","NAME");
bundle.putString("Key_Salary",Salary);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
intent.setClass(this,NewActivity.class);
startActivity();
//從intnet中獲取數據
Bundle bundle = this.getIntent().getExtras(); //get bundle
String name = bundle.getString("Key_Name");
String salary = bundle.getString("Key_Salaray");
setTitle(name+'-'+salary);
另外一種在Activity間傳遞數據的方式intnet把服務請 求發送到目標Activity,在源請求Activity中沖在onActivity()方法等待Intent返回應答結果。
startActivity(intent,REQUEST_ASK);//開啟intent時同時捎帶上請求
//重載onActivityResult()
void onActivityResult(int requestCode,int resultCode,Intent data){
super.onActivityResult(requestCode,resultCode,data);
if(requestCode == REQUEST_ASK){
if(reulstCode == RESULT_CANCELed){
setTitle("cancel...");
}else if(ResultCode == RESULT_OK){
showBundle = data.getExtras();
Name = Bundle.getString("myName");
}
}
}
目標Activity中發送結果代碼,連同源請求的數據一起綁定到Bundle中通過Intent傳回請求activity中去。
bundle.putString("Name",NAME);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
setResult(RESULT_OK,intent);//通過Intent返回結果
finish();
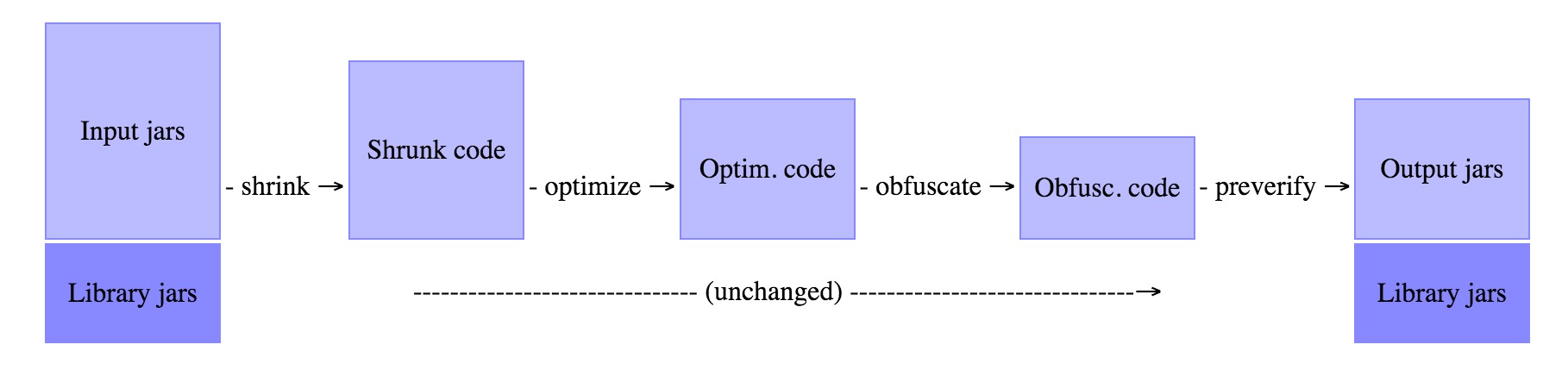 Android代碼混淆ProGuard工作原理簡介
Android代碼混淆ProGuard工作原理簡介
ProGuard能夠對Java類中的代碼進行壓縮(Shrink),優化(Optimize),混淆(Obfuscate),預檢(Preveirfy)。 1. 壓縮(Sh
 Android 自定義view實現水波紋動畫效果
Android 自定義view實現水波紋動畫效果
在實際的開發中,很多時候還會遇到相對比較復雜的需求,比如產品妹紙或UI妹紙在哪看了個讓人興奮的效果,興致高昂的來找你,看了之後目的很明確,當然就是希望你能給她;在這樣的關
 Android UI開發神兵利器之Android Action Bar Style Generator
Android UI開發神兵利器之Android Action Bar Style Generator
ActionBar是3.0後的UI設計規范,同時也是Google極力推薦使用的設計風格,如何快速設計一個入眼的ActionBar呢,更進一步,給我們搭好一個入眼的Acti
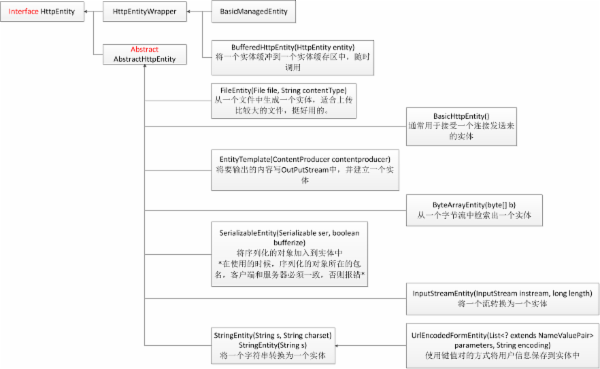 AndroidHttpClient詳解及調用示例
AndroidHttpClient詳解及調用示例
下面給大家展示了AndroidHttpClient結構:public final classAndroidHttpClientextends Objectimplemen