編輯:關於Android編程
今天學習android VIEW的刷新機制,之前一直以為是調用VIEW的刷新就自己調用刷新函數。今天學習了一下view的刷新機制,還是表示學習到很多的知識啊。
感想就是自己要多閱讀android的源代碼,其實很多的消息傳遞等等的機制,都是通過閱讀android的源代碼得到的,所以有事沒事就去看源代碼玩吧~
好了,來到正題,關鍵的一句話就是:
在Android的布局體系中,父View負責刷新、布局顯示子View;而當子View需要刷新時,則是通知父View來完成。
步驟就是:
1、調用子View的invalidate()
2、跳轉到上一層的invalidateChild函數中區
3、在一次調用invalidateChildInParent的函數一次層層刷新
4、具體的刷新後續操作,我就不清楚了,調用invalidate最終在代碼上就在invalidateChild終止了的,所以表示有點點不清晰,求各位大牛介紹一下吧。。。。。?在此謝過了。。
讓我來閱讀源代碼:
首先在View類中:
/**
* Invalidate the whole view. If the view is visible, {@link #onDraw} will
* be called at some point in the future. This must be called from a
* UI thread. To call from a non-UI thread, call {@link #postInvalidate()}.
*/
public void invalidate() {
if (ViewDebug.TRACE_HIERARCHY) {
ViewDebug.trace(this, ViewDebug.HierarchyTraceType.INVALIDATE);
}
if ((mPrivateFlags & (DRAWN | HAS_BOUNDS)) == (DRAWN | HAS_BOUNDS)) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~DRAWN & ~DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
final ViewParent p = mParent; //獲得父類View的對象
final AttachInfo ai = mAttachInfo;//獲得匹配
if (p != null && ai != null) {
final Rect r = ai.mTmpInvalRect;
r.set(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop);//設置本View的尺寸,其實就是大小沒有設置位置
// Don't call invalidate -- we don't want to internally scroll
// our own bounds
p.invalidateChild(this, r); //調用父類的刷新函數
}
}
}
下面我們來到Viewgroup對象:
在invalidate中,調用父View的invalidateChild,這是一個從第向上回溯的過程,每一層的父View都將自己的顯示區域與傳入的刷新Rect做交集。
/**
* Don't call or override this method. It is used for the implementation of
* the view hierarchy.
*/
public final void invalidateChild(View child, final Rect dirty) {
if (ViewDebug.TRACE_HIERARCHY) {
ViewDebug.trace(this, ViewDebug.HierarchyTraceType.INVALIDATE_CHILD);
}
ViewParent parent = this;
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
if (attachInfo != null) {
final int[] location = attachInfo.mInvalidateChildLocation;
// 刷新子View的位置
location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX] = child.mLeft;
location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX] = child.mTop;
// If the child is drawing an animation, we want to copy this flag onto
// ourselves and the parent to make sure the invalidate request goes
// through
final boolean drawAnimation = (child.mPrivateFlags & DRAW_ANIMATION) == DRAW_ANIMATION;
// Check whether the child that requests the invalidate is fully opaque
final boolean isOpaque = child.isOpaque() && !drawAnimation &&
child.getAnimation() != null;
// Mark the child as dirty, using the appropriate flag
// Make sure we do not set both flags at the same time
final int opaqueFlag = isOpaque ? DIRTY_OPAQUE : DIRTY;
do {
View view = null;
if (parent instanceof View) {
view = (View) parent;
}
if (drawAnimation) {
if (view != null) {
view.mPrivateFlags |= DRAW_ANIMATION;
} else if (parent instanceof ViewRoot) {
((ViewRoot) parent).mIsAnimating = true;
}
}
// If the parent is dirty opaque or not dirty, mark it dirty with the opaque
// flag coming from the child that initiated the invalidate
if (view != null && (view.mPrivateFlags & DIRTY_MASK) != DIRTY) {
view.mPrivateFlags = (view.mPrivateFlags & ~DIRTY_MASK) | opaqueFlag;
}
parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty);
} while (parent != null);
}
/**
* Don't call or override this method. It is used for the implementation of
* the view hierarchy.
*
* This implementation returns null if this ViewGroup does not have a parent,
* if this ViewGroup is already fully invalidated or if the dirty rectangle
* does not intersect with this ViewGroup's bounds.
*/ www.2cto.com
public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(final int[] location, final Rect dirty) {
if (ViewDebug.TRACE_HIERARCHY) {
ViewDebug.trace(this, ViewDebug.HierarchyTraceType.INVALIDATE_CHILD_IN_PARENT);
}
if ((mPrivateFlags & DRAWN) == DRAWN) {
if ((mGroupFlags & (FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE | FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE)) !=
FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE) {
// 由父類的的位置,偏移刷新區域
dirty.offset(location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX] - mScrollX,
location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX] - mScrollY);
final int left = mLeft;
final int top = mTop;
if (dirty.intersect(0, 0, mRight - left, mBottom - top) ||
(mPrivateFlags & DRAW_ANIMATION) == DRAW_ANIMATION) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX] = left;
location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX] = top;
return mParent;
}
} else {
mPrivateFlags &= ~DRAWN & ~DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX] = mLeft;
location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX] = mTop;
dirty.set(0, 0, mRight - location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX],
mBottom - location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX]);
return mParent;
}
}
return null;
}
另外:
Invalidate()方法不能放在線程中,所以需要把Invalidate()方法放在Handler中。在MyThread中只需要在規定時間內發送一個Message給handler,當Handler接收到消息就調用Invalidate()方法。
postInvalidate()方法就可以放在線程中做處理,就不需要Handler。
而上面的新線程MyThre可以放在OnCreate()中開始,也可以放在OnStart()中開始。
Invalidate()方法和postInvalidate()都可以在主線程中調用而刷新視圖。
Invalidate()方法在SDK中是這樣描述的:Invalidate the whole view. If the view is visible, onDraw(Canvas) will be called at some point in the future. This must be called from a UI thread. To call from a non-UI thread, call postInvalidate(). 當Invalidate()被調用的時候,View的OnDraw()就會被調用,Invalidate()必須是在UI線程中被調用,如果在新線程中更新視圖的就調用postInvalidate()。
 Android Dialog 設置字體大小的具體方法
Android Dialog 設置字體大小的具體方法
先看下面圖片:這是我在做登錄頁面的時候,調用系統的ProgressDialog 進行等待,可是看起來很不協調,左邊的等待圖片過大,右邊文字過小,看起來老別扭,雖然功能上不
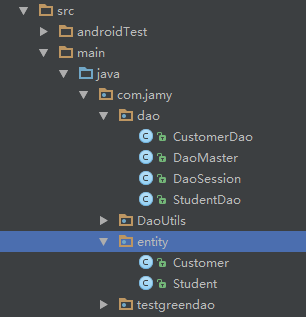 GreenDao的實用封裝
GreenDao的實用封裝
前面簡單介紹了下GreenDao的使用,從前面的介紹看來是不是覺得有點 so easy。對就是這麼簡單。曾經有位大神說作為一位合格的程序員就要在學習別人的東西時,有點自己
 Android開發教程之shape和selector的結合使用
Android開發教程之shape和selector的結合使用
shape和selector是Android UI設計中經常用到的,比如我們要自定義一個圓角Button,點擊Button有些效果的變化,就要用到shape和select
 Android Timer使用的實例代碼
Android Timer使用的實例代碼
1:服務端使用PHP 復制代碼 代碼如下:<?php echo date(Y-m-d H:i:s);?>2:activit