編輯:關於Android編程
這篇文章沒有什麼可看性,主要是源碼注釋太多,推薦自己看源碼,更容易理解些,在這裡主要介紹,其運作流程,貼代碼片段。
自定義View要重寫三個方法:onMeasure,onLayout,onDraw,這三個方法各有個的作用,onMeasure是對組件的寬高進行測量,onLayout是對子控件的位置進行擺放,onDraw是對自定義控件進行繪制,已經對onMeasure,onLayout方法進行了運用,那個源碼注釋也很多,如果有興趣的可以去看看,本章是對onDraw方法進行使用,順帶使用Path對象。
好了,先談談為什麼我要重復造輪子,要做一個有簽到功能的日歷,由於自己對自定義的組件ondraw方法還沒怎麼用過,所以重復造輪子咯,是不是理由不是很充分,沒關系,開心就好。
先來張效果圖
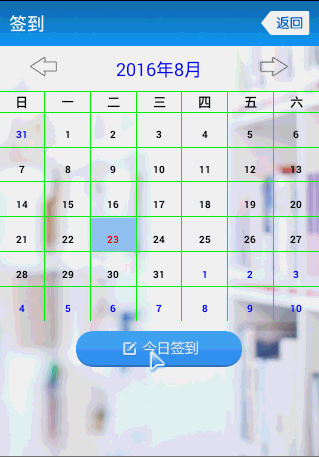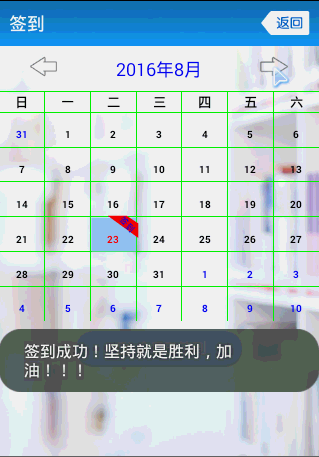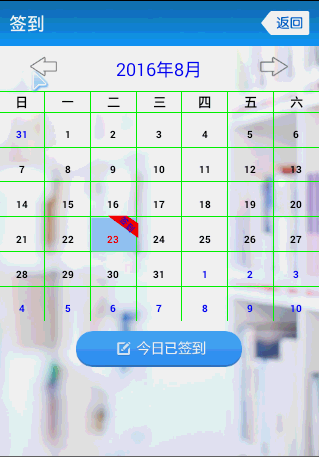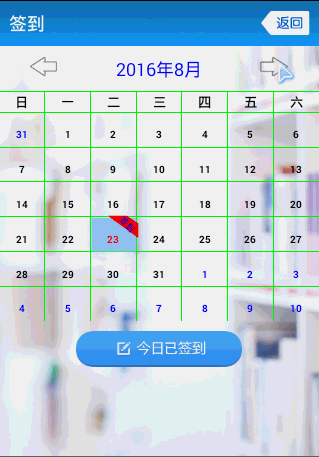
這個CalendarView的API
String clickLeftMonth(); //上一個月 return String(年-月)
String clickRightMonth(); //下一個月 return String(年-月)
Surface getSurface(); //獲取整個組件畫圖對象,可進行設置字體顏色等 return Surface
String getYearAndmonth(); // 獲得當前應該顯示的年月 return String(年-月)
boolean isSelectMore(); //返回是否多選
setSelectMore(boolean flag);//設置是否多選
setFlagData(String[] flags);//設置要進行標記的數據
setOnItemClickListener(OnItemClickListener); //點擊一個日期的回調事件
setWritingFlag(String str); //設置標記字符,默認為簽到
OK,先來簡述下這個組件跑起來的流程,
1.初始化數據。
2.測量組件大小,即調用了OnMeasure方法
3.調用onDraw方法。
步驟是不是很簡單呀?OK,通過源碼簡單的跑一下流程。
public CalendarView(Context context) {
super(context);
// 初始化數據
init();
}
public CalendarView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// 初始化數據
init();
}
/**
* 初始化數據 ,初始化事件對象 ,初始化日期格式類對象 ,Surface布局對象初始化 ,獲取屏幕密度比例 ,設置View背景 ,設置觸摸事件
*/
private void init() {
// 創建一個Date對象並將引用給顯示的月,選擇開始,選擇結束,今天的日期
curDate = selectedStartDate = selectedEndDate = today = new Date();
// 獲取一個日期類對象
calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
// 設置日期
calendar.setTime(curDate);
// 創建一個布局路徑
surface = new Surface(this);
// 獲取屏幕密度比例
surface.density = getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
// 給整個控件設置觸摸事件
setOnTouchListener(this);
}
這一塊看出,在組件進行實例化的時候調用了init方法,然後看見了new Surface() 創建了一個Surface對象。ok來看下這個Surface類,其他的應該都知道是什麼。(像我注釋這麼密的看不懂才怪(*\^__^*))。
public void init() {
float temp = height / 7f;// 將整個視圖分成了7份,每份所占的高度
monthHeight = 0;// (float) ((temp + temp * 0.3f) * 0.6);
weekHeight = (float) ((temp + temp * 0.3f) * 0.5);
cellHeight = (height - monthHeight - weekHeight) / 6f;
cellWidth = width / 7f;
// 創建一個邊框的畫筆並設置其屬性
borderPaint = new Paint();
borderPaint.setColor(cellBorderColor);
borderPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
// 邊框的寬度
borderWidth = (float) (0.5 * density);
borderWidth = borderWidth < 1 ? 1 : borderWidth;
borderPaint.setStrokeWidth(borderWidth);
// 創建星期畫筆並設置其屬性
weekPaint = new Paint();
weekPaint.setColor(textWeekColor);
weekPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
float weekTextSize = weekHeight * 0.6f;
weekPaint.setTextSize(weekTextSize);
weekPaint.setTypeface(Typeface.DEFAULT_BOLD);
// 創建時間畫筆並設置其屬性
datePaint = new Paint();
datePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
float cellTextSize = cellHeight * 0.3f;
datePaint.setTextSize(cellTextSize);
datePaint.setTypeface(Typeface.DEFAULT_BOLD);
// 創建一個Path對象用於記錄畫筆所畫的路徑
boxPath = new Path();
// 畫第一行,現在起點是0,0
boxPath.rLineTo(width, 0);
// 將起點向下移動一個星期格子的高度
boxPath.moveTo(0, monthHeight + weekHeight);
// 畫第二行
boxPath.rLineTo(width, 0);
// 循環畫縱線和號數的橫線
for (int i = 1; i < 7; i++) {
// 縱線
boxPath.moveTo(i * cellWidth, monthHeight);
boxPath.rLineTo(0, height - monthHeight);
// 橫線
boxPath.moveTo(0, monthHeight + weekHeight + i * cellHeight);
boxPath.rLineTo(width, 0);
}
// 表格被選擇後使用的畫筆
cellBgPaint = new Paint();
cellBgPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
cellBgPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
cellBgPaint.setColor(cellSelectBgColor);
}
其實這個類也沒做什麼,就一個init方法就是初始化各種畫筆,然後動態計算各種高度和寬度。這裡面的那個for循環裡面的boxPath就是通過path對象記錄繪制的表格路徑。
ok回到CalendarView類,這個組件被實例化了,就開始進行調用onMeasure方法了。這方法裡面沒啥可說的就是測量這個組件的大小,確定這個組件需要的寬高是多少如果
onMeasure和onLayout會被執行兩次,然後才執行onDraw方法,看下這個onDraw方法。
首先調用了這個calculateDate方法。這個方法是動態計算日期的。
/**
* 計算日期,計算出上月,這月下月的日期裝入到一個數組裡面進行保存
*/
private void calculateDate() {
calendar.setTime(curDate);
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 1);
int dayInWeek = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
Log.d(TAG, "day in week:" + dayInWeek);
int monthStart = dayInWeek;
monthStart -= 1; // 以日為開頭-1,以星期一為開頭-2
curStartIndex = monthStart;
date[monthStart] = 1;
// last month
if (monthStart > 0) {
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 0);
int dayInmonth = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
for (int i = monthStart - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
date[i] = dayInmonth;
dayInmonth--;
}
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, date[0]);
}
showFirstDate = calendar.getTime();
// this month
calendar.setTime(curDate);
calendar.add(Calendar.MONTH, 1);
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 0);
int monthDay = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
for (int i = 1; i < monthDay; i++) {
date[monthStart + i] = i + 1;
}
curEndIndex = monthStart + monthDay;
// next month
for (int i = monthStart + monthDay; i < 42; i++) {
date[i] = i - (monthStart + monthDay) + 1;
}
if (curEndIndex < 42) {
// 顯示了下一月的
calendar.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 1);
}
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, date[41]);
showLastDate = calendar.getTime();
}
這個方法動態計算日期,顯示計算上個月所剩下的日期裝入數組date裡面,然後裝當前月份的,最後裝下個月開頭部分日期。
為什麼會在這個onDraw方法裡面調用呢,因為如果在構造方法裡面執行一次就沒法執行了,如果我點擊下一個月那數據就不變了,onMeasure和onLayout都執行兩遍所以不行。因此只能在onDraw方法繪制一次,計算一下。
往下看,這段代碼是繪制星期天的。
// 畫用於分隔顯示號數的表格框
canvas.drawPath(surface.boxPath, surface.borderPaint);
// 星期計算
float weekTextY = surface.monthHeight + surface.weekHeight * 3 / 4f;
// 繪制星期1.2.3等字體
for (int i = 0; i < surface.weekText.length; i++) {
float weekTextX = i
* surface.cellWidth
+ (surface.cellWidth - surface.weekPaint
.measureText(surface.weekText[i])) / 2f;
canvas.drawText(surface.weekText[i], weekTextX, weekTextY,
surface.weekPaint);
}
動態計算星期1-7的位置然後在所處位置繪制文字。
再下面就是繪制選擇格子的背景顏色,默認是當前月的當前號數。
/**
* @param canvas
*/
private void drawDownOrSelectedBg(Canvas canvas) {
// down and not up
if (downDate != null) {
drawCellBg(canvas, downIndex, surface.cellDownBgColor);
}
// selected bg color
if (!selectedEndDate.before(showFirstDate)
&& !selectedStartDate.after(showLastDate)) {
int[] section = new int[]{-1, -1};
calendar.setTime(curDate);
calendar.add(Calendar.MONTH, -1);
findSelectedIndex(0, curStartIndex, calendar, section);
if (section[1] == -1) {
calendar.setTime(curDate);
findSelectedIndex(curStartIndex, curEndIndex, calendar, section);
}
if (section[1] == -1) {
calendar.setTime(curDate);
calendar.add(Calendar.MONTH, 1);
findSelectedIndex(curEndIndex, 42, calendar, section);
}
if (section[0] == -1) {
section[0] = 0;
}
if (section[1] == -1) {
section[1] = 41;
}
for (int i = section[0]; i <= section[1]; i++) {
drawCellBg(canvas, i, surface.cellSelectBgColor);
}
}
}
後面就是開始繪制日期,即將畫出來的表格填充數字。
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
// 這個月的字體顏色
int color = surface.textInstantColor;
if (isLastMonth(i)) {
// 上個月字體顏色
color = surface.textOtherColor;
} else if (isNextMonth(i)) {
// 下個月字體顏色
color = surface.textOtherColor;
} else if (todayIndex != -1) {
// 循環為簽到的日期加標記
int flagLen = flagData == null ? 0 : flagData.length;
for (int j = 0; j < flagLen; j++) {
if ((date[i] + "").equals(flagData[j]))
drawCellFlag(canvas, i, surface.textFlagBgColor,
surface.textFlagColor);
}
// 如果todayIndex不等於-1且等於今天
if (i == todayIndex) {
// 今天字體顏色
color = surface.textTodayColor;
}
}
drawCellText(canvas, i, date[i] + "", color);
}
在這值得一提的就是這個添加簽到標簽的方法drawCellFlag。
/**
* 在格子的右上角進行繪制標簽
*
* @param canvas 畫布
* @param index 下標
* @param bgcolor 背景顏色
* @param textcolor 字體顏色
*/
private void drawCellFlag(Canvas canvas, int index, int bgcolor,
int textcolor) {
int x = getXByIndex(index);
int y = getYByIndex(index);
// 計算一個方格子的上下左右距離組件邊框的距離,以此來推出其坐標
float left = surface.cellWidth * (x - 1) + surface.borderWidth;
float top = surface.monthHeight + surface.weekHeight + (y - 1)
* surface.cellHeight - surface.borderWidth;
float right = left + surface.cellWidth + surface.borderWidth;
float botton = top + surface.cellHeight - surface.borderWidth;
surface.cellBgPaint.setColor(bgcolor);
// 通過Path來記錄路徑,畫一個梯形圖
Path path = new Path();
path.moveTo(right - surface.cellWidth * 2 / 3, top);
path.lineTo(right - surface.cellWidth / 4, top);
path.lineTo(right, botton - surface.cellHeight * 3 / 4);
path.lineTo(right, botton - surface.cellHeight / 3);
canvas.drawPath(path, surface.cellBgPaint);
// 因為下面的繪制的文字將要進行旋轉因此我將以上Canvas繪制的圖案進行保存,這樣就不會被旋轉給影響到了
canvas.save();
// 將字體進行旋轉40度,以文字開始繪制的坐標點進行旋轉
canvas.rotate((float) 45, right - surface.cellWidth * 3 / 7, botton
- surface.cellHeight * 5 / 6);
surface.cellBgPaint.setColor(textcolor);
// 動態的計算字體大小
float a = surface.cellWidth / 4;
float b = surface.cellHeight / 4;
float c = (float) Math.sqrt(a * a + b * b);
surface.cellBgPaint.setTextSize(c * 3 / 5);
surface.cellBgPaint.setTypeface(Typeface.DEFAULT_BOLD);
// 繪制文字
canvas.drawText(writingFlag, right - surface.cellWidth * 3 / 7, botton
- surface.cellHeight * 5 / 6, surface.cellBgPaint);
// 釋放旋轉狀態,恢復sava時的狀態
canvas.restore();
}
這個方法裡面能計算出每個表格的left,right,top,botton的位置,即就可以動態計算梯形四個點,這四個點就是
A(right - surface.cellWidth * 2 / 3, top)
B(right - surface.cellWidth / 4, top)
C(right, botton - surface.cellHeight * 3 / 4)
D(right, botton - surface.cellHeight / 3)
通過Path對象記錄這四個點串起來的路徑然後canvas繪制就ok了。
而這個標簽“簽到”的位置也是這樣給算出來的。
ok,大概流程講完了。詳細的可以去看源碼,裡面注釋多多,你一定能看懂的。(*^__^*)。
 android動態設置app當前運行語言
android動態設置app當前運行語言
android開發中有時候碰到切換語言的需求,這時候需要通過代碼動態改變當前運行語言。 package com.example.androidtest; import
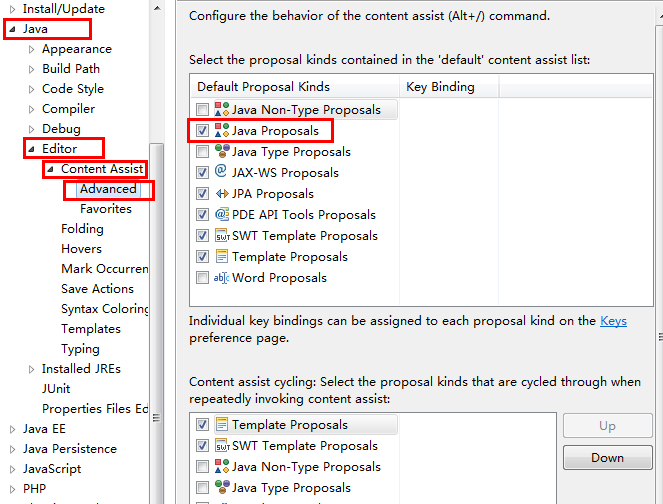 android開發 eclipse alt+”/”自動提示失效的解決方法
android開發 eclipse alt+”/”自動提示失效的解決方法
1、用於沒有一點提示的情況:依次打開eclipse上面的windows ——preferences ——java ——editor —— content assist ,
 Android之後台啟動Activity
Android之後台啟動Activity
在實際開發中,Activity需要啟動但界面又不能顯示出來,這時就需要後台啟動,但又不是finish(),這時就要用到Activity中的moveTaskToBack函數
 Android提供的系統服務之--AlarmManager(鬧鐘服務)
Android提供的系統服務之--AlarmManager(鬧鐘服務)
本節引言: 本節主要介紹的是Android系統服務中的---AlarmManager(鬧鐘服務), 除了開發手機鬧鐘外,更多的時候是作為一個全