編輯:關於Android編程
GLSurfaceView提供了下列特性:
1> 管理一個surface,這個surface就是一塊特殊的內存,能直接排版到android的視圖view上。
2> 管理一個EGL display,它能讓opengl把內容渲染到上述的surface上。
3> 用戶自定義渲染器(render)。
4> 讓渲染器在獨立的線程裡運作,和UI線程分離。
5> 支持按需渲染(on-demand)和連續渲染(continuous)。
6> 一些可選工具,如調試。
概念:
Display(EGLDisplay) 是對實際顯示設備的抽象。
Surface(EGLSurface)是對用來存儲圖像的內存區域FrameBuffer的抽象,包括Color Buffer, Stencil Buffer ,Depth Buffer.
Context (EGLContext) 存儲OpenGL ES繪圖的一些狀態信息。
步驟:
獲取EGLDisplay對象
初始化與EGLDisplay 之間的連接。
獲取EGLConfig對象
創建EGLContext 實例
創建EGLSurface實例
連接EGLContext和EGLSurface.
使用GL指令繪制圖形
斷開並釋放與EGLSurface關聯的EGLContext對象
刪除EGLSurface對象
刪除EGLContext對象
終止與EGLDisplay之間的連接。
GLSurfaceView的繪制流程
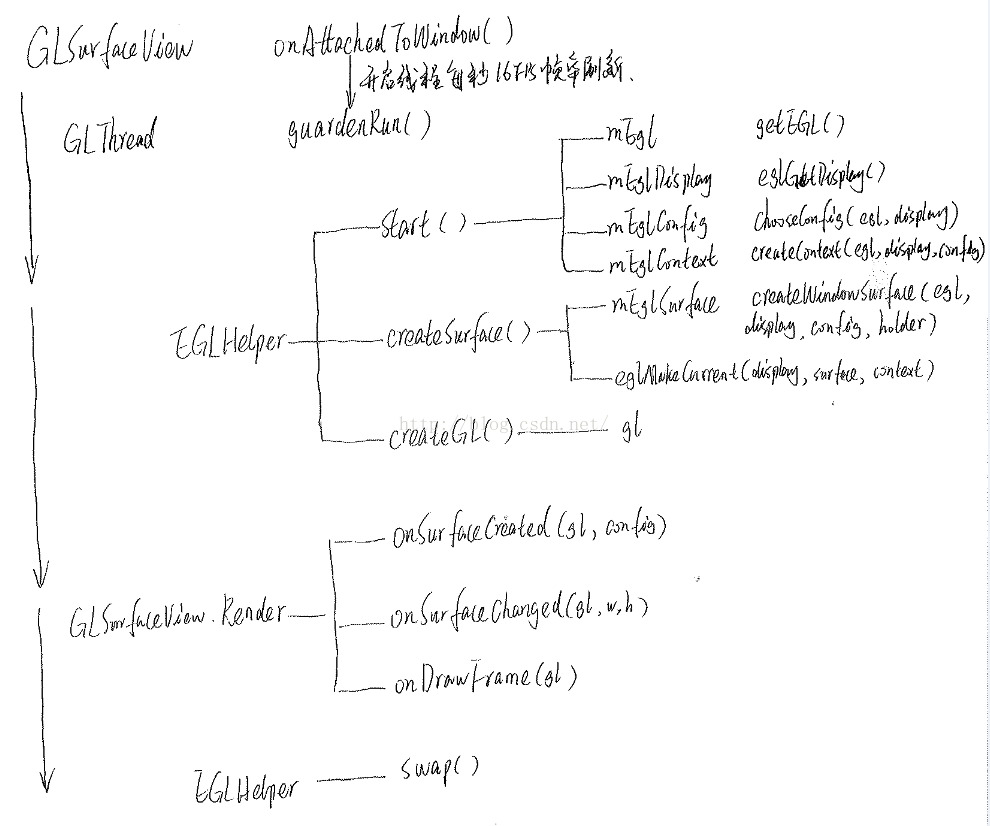
由上圖可知,GLSurfaceView的主要繪制過程都是在一個子線程中完成,即整個繪制最終都是guardenRun()中完成。在這個過程中完成了整個EGL繪制的所有步驟。
我把guardenRun()的大多數細節代碼都刪掉了,剩下一些精華:
private void guardedRun() throws InterruptedException {
while (true) {
synchronized (sGLThreadManager) {
while (true) {
// Ready to draw?
if (readyToDraw()) {
// If we don't have an EGL context, try to acquire one.
if (! mHaveEglContext) {
if (sGLThreadManager.tryAcquireEglContextLocked(this)) {
mEglHelper.start();
}
}
sGLThreadManager.wait();
}
} // end of synchronized(sGLThreadManager)
if (createEglSurface) {
if (mEglHelper.createSurface()) {
...
}
}
if (createGlInterface) {
gl = (GL10) mEglHelper.createGL();
}
if (createEglContext) {
if (view != null) {
view.mRenderer.onSurfaceCreated(gl, mEglHelper.mEglConfig);
}
}
if (sizeChanged) {
if (view != null) {
view.mRenderer.onSurfaceChanged(gl, w, h);
}
sizeChanged = false;
}
if (view != null) {
view.mRenderer.onDrawFrame(gl);
}
int swapError = mEglHelper.swap();
}
public void start() {
/*
* Get an EGL instance
*/
mEgl = (EGL10) EGLContext.getEGL();
/*
* Get to the default display.
*/
mEglDisplay = mEgl.eglGetDisplay(EGL10.EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
mEglConfig = view.mEGLConfigChooser.chooseConfig(mEgl, mEglDisplay);
/*
* Create an EGL context. We want to do this as rarely as we can, because an
* EGL context is a somewhat heavy object.
*/
mEglContext = view.mEGLContextFactory.createContext(mEgl, mEglDisplay, mEglConfig);
}
1,獲取EGLDisplay對象
2,初始化與EGLDisplay 之間的連接。
3,獲取EGLConfig對象
4,創建EGLContext 實例
請注意注解中提到createContext()創建的mEglContext是一個重量級對象,在創建的時候很耗資源,我們盡可能少的創建它。所以,在guardenRun()中我們做了對mEglContext的是否存在的判斷:
if (! mHaveEglContext) {
if (sGLThreadManager.tryAcquireEglContextLocked(this)) {
mEglHelper.start();
}
}
/**
* Create an egl surface for the current SurfaceHolder surface. If a surface
* already exists, destroy it before creating the new surface.
*
* @return true if the surface was created successfully.
*/
public boolean createSurface() {
if (view != null) {
mEglSurface = view.mEGLWindowSurfaceFactory.createWindowSurface(mEgl,
mEglDisplay, mEglConfig, view.getHolder());
}
/*
* Before we can issue GL commands, we need to make sure
* the context is current and bound to a surface.
*/
if (!mEgl.eglMakeCurrent(mEglDisplay, mEglSurface, mEglSurface, mEglContext)) {
/*
* Could not make the context current, probably because the underlying
* SurfaceView surface has been destroyed.
*/
return false;
}
return true;
}
這裡主要完成了兩件事:
5,創建mEglSurface,這個代表了將要被渲染的那段內存。請注意到createWindowSurface()的四個參數,尤其是最後一個參數view.getHolder()。
createSurface()上面有一句注解:Create an egl surface for the current SurfaceHolder surface.這個只能意會,很難言傳。我理解是被渲染後的mEglSurface也是為了給mSurface來呈現的。總之mEglSurface和mSurface之間一定有著很重要的關系的,在一定程度上你也可以理解他們代表著同一塊用來渲染的內存。
6,連接EGLContext和EGLSurface:eglMakeCurrent()。
7,使用GL指令繪制圖形
if (createGlInterface) {
gl = (GL10) mEglHelper.createGL();
}
if (createEglContext) {
if (view != null) {
view.mRenderer.onSurfaceCreated(gl, mEglHelper.mEglConfig);
}
}
if (sizeChanged) {
if (view != null) {
view.mRenderer.onSurfaceChanged(gl, w, h);
}
sizeChanged = false;
}
if (view != null) {
view.mRenderer.onDrawFrame(gl);
}
所以在實現Render看到的GL10 gl,就是從這裡傳過來的。
在整個guardenRun()過程中,你應該要發現一個很重要的點,這是一個無限循環的程序,而onDrawFrame(gl)幾乎是沒有設置任何障礙就可以每次循環都被觸發。而onDrawFrame(gl)的實現正是整個渲染的主體部分,由Render的子類來實現。
後面幾個步驟就不一一講訴了
8,斷開並釋放與EGLSurface關聯的EGLContext對象
9,刪除EGLSurface對象
10,刪除EGLContext對象
11,終止與EGLDisplay之間的連接。
在使用GlSurfaceView的時候,通常會繼承GLSurfaceView,並重載一些和用戶輸入事件有關的方法。如果你不需要重載事件方法,GLSurfaceView也可以直接使用, 你可以使用set方法來為該類提供自定義的行為。
說到這裡,我就上一個最簡化的demo:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private MyGLSurfaceView mGLView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
mGLView = new MyGLSurfaceView(this);
mGLView.setRenderer(new ClearRenderer());
setContentView(mGLView);
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
mGLView.onPause();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mGLView.onResume();
}
class ClearRenderer implements MyGLSurfaceView.Renderer {
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl, javax.microedition.khronos.egl.EGLConfig config) {
}
public void onSurfaceChanged (GL10 gl, int w, int h)
{
gl.glViewport(0, 0, w, h);
}
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) {
gl.glClearColor(mRed, mGreen, mBlue, 1.0f);
gl.glClear(GL10.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL10.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
}
}
}
GLSurfaceView的繪制過程要點
1,GLSurfaceview的渲染模式RenderMode
在onAttachedToWindow後就啟動了一個無線循環的子線程,該子線程完成了整個繪制流程,並系統默認是負責不斷刷新重繪,刷新的幀率是16FPS。從這裡也可以看出來,GLSurfaceView系統默認是60ms就重繪一次,這樣的耗性能的重繪操作一定是要用在那種有持續動畫的效果才有意義。
當然,你也可以通過設置setRenderMode去設置主動刷新:
/**
* Set the rendering mode. When renderMode is
* RENDERMODE_CONTINUOUSLY, the renderer is called
* repeatedly to re-render the scene. When renderMode
* is RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY, the renderer only rendered when the surface
* is created, or when {@link #requestRender} is called. Defaults to RENDERMODE_CONTINUOUSLY.
*
* Using RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY can improve battery life and overall system performance * by allowing the GPU and CPU to idle when the view does not need to be updated. *
* This method can only be called after {@link #setRenderer(Renderer)} * * @param renderMode one of the RENDERMODE_X constants * @see #RENDERMODE_CONTINUOUSLY * @see #RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY */ public void setRenderMode(int renderMode) { mGLThread.setRenderMode(renderMode); }
注解中提到:系統默認mode==RENDERMODE_CONTINUOUSLY,這樣系統會自動重繪;mode==RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY時,只有surfaceCreate的時候會繪制一次,然後就需要通過requestRender()方法主動請求重繪。同時也提到,如果你的界面不需要頻繁的刷新最好是設置成RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY,這樣可以降低CPU和GPU的活動,可以省電。
2,事件處理
為了處理事件,一般都是繼承GLSurfaceView類並重載它的事件方法。但是由於GLSurfaceView是多線程操作,所以需要一些特殊的處理。由於渲染器在獨立的渲染線程裡,你應該使用Java的跨線程機制跟渲染器通訊。queueEvent(Runnable)方法就是一種相對簡單的操作。
class MyGLSurfaceView extends GLSurfaceView {
private MyRenderer mMyRenderer;
public void start() {
mMyRenderer = ...;
setRenderer(mMyRenderer);
}
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER) {
queueEvent(new Runnable() {
// 這個方法會在渲染線程裡被調用
public void run() {
mMyRenderer.handleDpadCenter();
}});
return true;
}
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);
}
}
}
調用queueEvent就是給隊列中添加runnable
public void queueEvent(Runnable r) {
synchronized(sGLThreadManager) {
mEventQueue.add(r);
sGLThreadManager.notifyAll();
}
}
if (! mEventQueue.isEmpty()) {
event = mEventQueue.remove(0);
break;
}
...
if (event != null) {
event.run();
event = null;
continue;
}
因為每次都會remove掉添加的runnable,所以上面那個demo就是非常好的解釋,每次按鍵就是添加runnable。當然,這也是要求繪制是一直在循環重繪的狀態才能看到效果。
關於GLSurfaceView的渲染過程的重要知識點已經介紹完畢,了解這些對開發當然是很有用的,很多時候你需要實現自定義的類GLSurfaceView的類。
那麼現在,最後剩下的就是onDrawFrame(GL10 gl)的主體繪制的實現,這也是最重要的一個部分,因為涉及的內容較多,就不在這裡陳述了。這裡使用的就是opengl的繪制引擎進行渲染操作,跟之前View的渲染是使用的Skia渲染引擎。
還記得View的繪制onDraw(Canvas canvas)嗎,對比onDrawFrame(GL10 gl),我想你該知道區別了。一個使用Skia引擎渲染,一個使用opengl引擎渲染。
問題:
1,GLSurfaceView繼承了SurfaceView,它自己的mEglSurface和從父類繼承的mSurface之間的關系?
但是呢,
mEglSurface = view.mEGLWindowSurfaceFactory.createWindowSurface(mEgl,
mEglDisplay, mEglConfig, view.getHolder());
mEglSurface在創建的時候,是有view.getHolder作為輸入的,我們知道SurfaceHolder是持有Surface的。我一直跟蹤到android_opengl_EGL14.cpp和com_google_android_gles_jni_EGLImpl.cpp 發現:surface總是作為一種輸入後再加上其他參數,才能返回mEglSurface。我就開始懷疑他們是不是同一個surface,他們是不是指向了同一快內存地址?
為了驗證我的這個想法,於是我打印了mSurface和mEglSurface的地址,發現他們卻不是同一塊地址。這就讓人深思了,現在的情況只能說明,他們兩個一定有關系,但是又不是指向同一塊地址。對這方面有經驗的朋友歡迎指導。
 UI高級--觸摸與手勢
UI高級--觸摸與手勢
1.觸摸事件的處理方式 (1)事件類型 觸摸事件(觸摸手機屏幕) 運動事件(如微信的搖一搖) 遠程控制事件(如藍牙)(2)響應者類通過復寫以下方法
 Android開發筆記(一百一十二)開發工具
Android開發筆記(一百一十二)開發工具
Eclipse/ADTADT是Google在Eclipse基礎上封裝了Android開發工具的環境,最新版本是2014年7月2日發布的adt-bundle-windows
 Android popupwindow 示例程序一
Android popupwindow 示例程序一
經過多番測試實踐,實現了popupwindow 彈出在指定控件的下方。代碼上有注釋,有需要注意的地方。popupwindow 有自已的布局,裡面控件的監聽實現都有。接下來
 Android 根據EditText搜索框ListView動態顯示數據
Android 根據EditText搜索框ListView動態顯示數據
根據EditText搜索框ListView動態顯示數據是根據需求來的,覺得這之中涉及的東西可能比較的有意思,所以動手來寫一寫,希望對大家有點幫助。首先,我們來分析下整個過