編輯:Android開發教程
今天開始接觸和熟悉Android上層應用,學海無涯,回頭是岸 -_-||
三種常見布局方法:Linearlayout(線性布局)、TableLayout?(表格布局)、Relative Layout(相對布局)。
相對布局比起前面兩種布局方法而言更隨意,用戶可以將控件放在自己所希望的任何位置。
在LinearLayout和TableLayout中常見的指令有
android:id——控件指定相應ID
android:text——控件中顯示文字。注意盡量使用Strings.xml
android:gravity——控件中文字基本位置,如center、left、right、center_horizontal等。
android:textsize——控件中字體大小,單位為pt。
android:background——控件背景色
android:width——控件寬度
android:height——控件高度
android:padding——空間內邊距,指控件當中內容到空間的距離。其中有android:padding_left、android:padding_right等。
android:siglelise——如果設置為真,控件內容將在同一行顯示。
android:margin——外邊距。
相對布局Relative Layout
android:Layout_above——將控件底部至於給定控件之上
android:Layout_below——將控件頂部至於給定控件之下
android:Layout_toleftof——將控件左邊緣至於給定控件右邊
android:Layout_toRightof——將控件左邊緣至於給定控件右邊
android:Layout_alignBaseline——將控件的Baseline與指定控件的Baseline對齊。
android:Layout_alignleft——將控件的左邊與指定控件的左邊對齊。
android:Layout_alignright——將控件的右邊與指定控件右邊對齊。
android:Layout_alignTop——將控件的頂部與指定控件頂部對齊。
android:Layout_alignParentBottom——為真,控件與父控件對齊。
android:Layout_centerHorizontal——為真,空間被至於水平方向中央。
android:Layout_centerinParent——為真,至於父控件水平/垂直方向中央。
android:Layout_centervertural——被置於垂直方向中央。
intent-filter
1 android.intent.action.MAIN決定應用程序最先啟動的Activity。
2 android.intent.category.LAUNCHER決定應用程序是否顯示在程序列表裡。
intent調用應用程序
例子: 調用Google浏覽器
Uri uri = Uri.parse("http://www.android123.com.cn");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW,uri);
startActivity(it);
常用的應用程序調用
顯示web網頁:
1. Uri uri = Uri.parse("http://www.android123.com.cn");
2. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW,uri);
3. startActivity(it);
顯示google地圖:
1. Uri uri = Uri.parse("geo:38.899533,-77.036476");
2. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.Action_VIEW,uri);
3. startActivity(it);
 android FragmentTabhost實現選項卡
android FragmentTabhost實現選項卡
在Android3.0之後,google創造了Fragment,因此原來的Tabhost已經不推薦使用了,現在一般推薦使用FragmentTabhost。google考慮
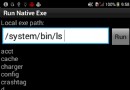 android技巧:如何在android程序中執行adb shell命令
android技巧:如何在android程序中執行adb shell命令
package net.gimite.nativeexe; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.F
 面向Android應用程序的基於Parse雲的服務
面向Android應用程序的基於Parse雲的服務
Parse 移動 SDK 為 iOS、Android 和 Windows 應用程序提供了基於雲的 API 和服務。Parse SDK 還提供 了 JavaScript 和
 Android開發入門(二十)內容提供者 20.1 數據共享
Android開發入門(二十)內容提供者 20.1 數據共享
在上一章節中,我們介紹了數據持久化的幾種方法:首選項,文件,以及數據庫。在保存復雜的數據結構 時,推薦使用SQliteDatabase。但是,共享數據就成了一種挑戰,因為