編輯:Android開發教程
Roboguice 提供了對Context 生命周期相關的事件的send 和receive ,系統缺 省支持的事件為:
OnActivityResultEvent
OnConfigurationChangedEvent
OnContentC hangedEvent
OnContentViewAvailableEvent
OnCreateEvent
OnDestroyEv ent
OnNewIntentEvent
OnPauseEvent
OnRestartEvent
OnResumeEvent< p>OnStartEvent
OnStopEvent
一個簡單的例子如下:
public
class MyActivity extends RoboActivity {
// You must "register" your listener in the current
// context by injecting it.
// Injection is commonly done here in the activity,
//but can also be done anywhere really.
@Inject protected MyListeners myListeners;
}
// In this example, all the listeners are in a
// MyListeners class, but really they could
// be anywhere as long as it's registered.
// You can even put the listeners directly into
// your activity classes if you like!
class MyListeners {
// Any method with void return type and a
// single parameter with @Observes annotation
// can be used as an event listener.
//This one listens to onResume.
public void doSomethingOnResume(
@Observes OnResumeEvent onResume ) {
Ln.d("Called doSomethingOnResume in onResume");
}
// As you might expect, some events can
//have parameters. The OnCreate event
// has the savedInstanceState parameter that
//Android passes to onCreate(Bundle)
public void doSomethingElseOnCreate(
@Observes OnCreateEvent onCreate ) {
Ln.d("onCreate savedInstanceState is %s",
onCreate.getSavedInstanceState())
}
// And of course, you can have multiple
//listeners for a given event.
// Note that ordering of listener execution
//is indeterminate!
public void xxx( @Observes OnCreateEvent onCreate ) {
Ln.d("Hello, world!")
}
}
有關Events的注意事項如下:
在Context中使用@Inject定義事件的 Listener.
Event只能在某一特定的Context(Activity)中傳送,不能跨 Context發送,接受。
Event除了提供上面列出的Context相關事件外,也可以 使用自定義的事件。
@observes 只能應用到方法上,而不能應用到構造函數上 。
下面使用一個自定義事件MyEvent,通過observer 這個自定義事件來發 送,接收自定義事件。
public
class EventDemo extends RoboActivity {
@Inject protected EventManager eventManager;
@InjectView (R.id.button) Button button;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.eventdemo);
button.setOnClickListener(mGoListener);
}
private OnClickListener mGoListener = new OnClickListener()
{
public void onClick(View v)
{
eventManager.fire(EventDemo.this,new MyEvent());
}
};
protected void handleEvent(@Observes MyEvent event){
Toast.makeText(this, "Custom event",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
class MyEvent{
//put any memeber you want here.
}
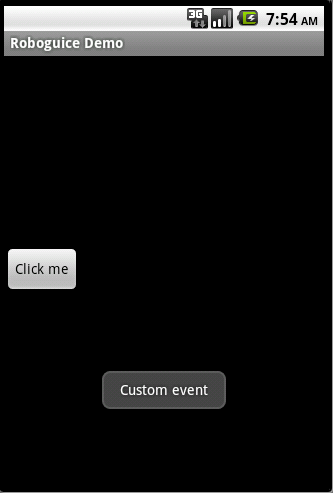
本例下載: http://www.imobilebbs.com/download/android/roboguice/EventDemo.zip
查看全套文章:http://www.bianceng.cn/OS/extra/201301/34950.htm
 效果很華麗的仿桌面APP
效果很華麗的仿桌面APP
開發Android APP的同學是否對於Launcher實現的絢麗效果而癡迷呢?什麼,連Android Launcher是什麼都不知道。好吧,拿起侬的手機,在解鎖後的首頁
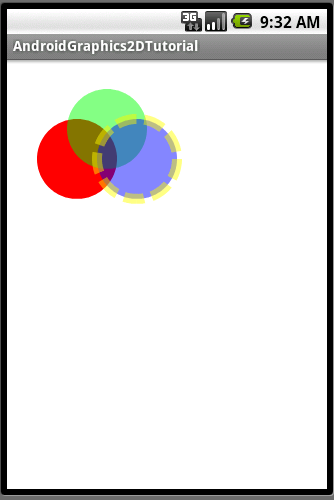 Android簡明開發教程八:引路蜂二維圖形繪制實例功能定義
Android簡明開發教程八:引路蜂二維圖形繪制實例功能定義
有了前面對Android平台的介紹,基本上可以開始編寫Android應用了,這裡將以繪制二維圖形為例,對Android開發的一般方 法做過介紹,其中涉及到自定義Appli
 Android碎片化圖表:果凍豆(Jelly Bean)領銜
Android碎片化圖表:果凍豆(Jelly Bean)領銜
又到了再一次審視Google家的移動操作系統"碎片化"到如何程度的時候了。OpenSignal背後的開發人員們,通過他們從用戶所下載的應用那裡收集來的
 Android實現進程間通信的實例
Android實現進程間通信的實例
Android Service是分為兩種:本地服務(Local Service): 同一個apk內被調用遠程服 務(Remote Service):被另一個apk調用遠程