編輯:Android開發教程
android中的context可以做很多操作,但是最主要的功能是加載和訪問資源。
在android中有兩種context,一種是 application context,一種是activity context,通常我們在各種類和方法間傳遞的是activity context。
比如一個 activity的onCreate:
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
getWindow().setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN);
setRequestedOrientation(ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT);
mGameView = new GameView(this);
setContentView(mGameView);
}
把activity context傳遞給view,意味著view擁有一個指向activity的引用,進而引用activity UI占有的資源: view , resource, SensorManager等。
但是這樣如果context發生內存洩露的話,就會洩露很多內存,這裡洩露的意思是gc沒 有辦法回收activity的內存(當前Activity為活動或finish後還沒來得及回收)。
Leaking an entire activity是很容易 的一件事。
當屏幕旋轉的時候,系統會銷毀當前的activity,保存狀態信息再創建一個新的。
比如我們寫了一個應用 程序,需要加載一個很大的圖片,我們不希望每次旋轉屏幕的時候都銷毀這個圖片重新加載。
實現這個要求的簡單想法 就是定義一個靜態的Drawable,這樣Activity 類創建銷毀它始終保存在內存中,訪問速度會很快。
實現類似:
public class myactivity extends Activity {
private static Drawable sBackground;
protected void onCreate(Bundle state) {
super.onCreate(state);
TextView label = new TextView(this);
label.setText("Leaks are bad");
if (sBackground == null) {
sBackground = getDrawable(R.drawable.large_bitmap);
}
label.setBackgroundDrawable(sBackground);//drawable attached to a view
setContentView(label);
}
}
 Android的資源(resource)簡介
Android的資源(resource)簡介
Android的應用程序(app)資源存儲在項目層次中的res文件夾下;資源的類型包括值(value),Drawable,顏色(color),布局(layout), 動畫
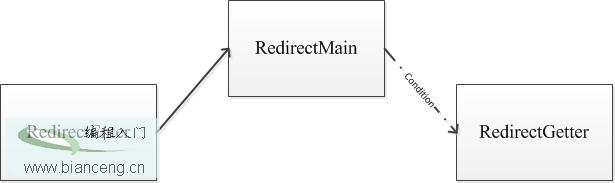 Android ApiDemos示例解析(12) App->Activity->Redirection
Android ApiDemos示例解析(12) App->Activity->Redirection
Redirection示例涉及到三個Acitivity: RedirectEnter, RedirectMain,RedirectGetter。示例的主Activity為
 Android UI設計與開發教程 引導界面(一)ViewPager介紹和使用詳解
Android UI設計與開發教程 引導界面(一)ViewPager介紹和使用詳解
做Android開發加起來差不多也有一年多的時間了,總是想寫點自己在開發中的心得體會與大家一起交流分 享、共同進步,剛開始寫也不知該如何下手,仔細想了一下,既然是剛開始
 Android中自定義控件讓TextView的drawableLeft與文本一起居中
Android中自定義控件讓TextView的drawableLeft與文本一起居中
前言TextView的drawableLeft、drawableRight和drawableTop是一個常用、好用的屬性,可以在文本的上下左右放置一個圖片,而不使用更加復