編輯:Android開發教程
本例實現的功能和例子Android RoboGuice 使用指南(2):第一個例子Hello World一樣,所不同的是本例使用RoboGuice2.0 來實現。
下載新的RoboGuice庫,Roboguice2.0 庫有四個庫組成,如下圖所示:
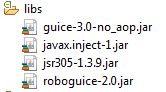
庫可以從 http://code.google.com/p/roboguice/下載。
2. 創建一個新Android項目,比如GuiceDemo,目標平台Android1.5以上。
3. 一般可以在該項目下添加一個libs目錄,將兩個jar文件拷到libs目 錄下,然後通過: Project > Properties > Java Build Path > Libraries > Add JARs
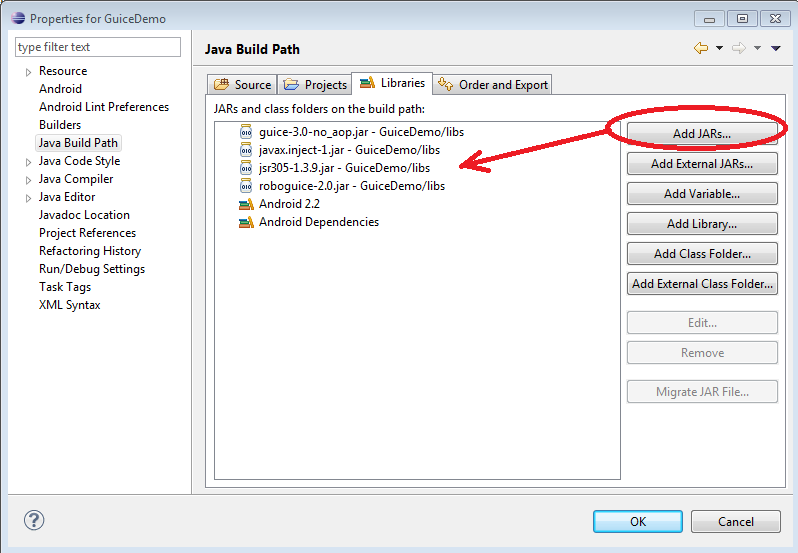
注:從ADT17開始,添加的jar文件需放在libs 子目錄下,可以參見升級到 ADT 17 出現dalvikvm: Unable to resolve superclass的問題
添加了對應guice 和roboguice庫的引用之後,就可以開始編寫第一個使用 roboguice2 的例子。
使用roboguice2 的步驟:
Roboguice2 中 不在含有RoboApplication 類,因此無需也不可能派生RoboApplication的子類 。這裡重復一下HelloWorld 的Layout 和類說明
1. 在這個簡單的例子中 ,它使用的Layout 定義如下:
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=” utf-8″?>
< LinearLayout xmlns:android=” http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
android:orientation=” vertical”
android:layout_width=”fill_parent”
android:layout_height=”fill_parent”
>
<TextView
android:id=”@+id/hello”
android:layout_width=”fill_parent”
android:layout_height=” wrap_content”
android:text=”@string/hello”
/>
< /LinearLayout>
我們定義了一個TextView ,它的id為hello.
假定 這個應用使用一個IGreetingService ,它有一個方法getGreeting() 返回一個字 符串,至於IGreetingService 如何實現,GuideDemo 不需要關心。
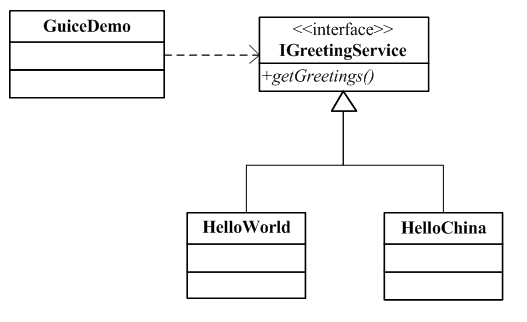
Dependency injection 設計模式的一個 核心原則為: Separate behavior from dependency resolution. 也就說將應用 需要實現的功能和其所依賴的服務或其它對象分離。 對本例來說GuiceDemo只要 知道它依賴於IGreetingService 服務,至於IGreetingService有誰實現 GuiceDemo並不需要知道。
在Roboguice 中使用@Inject 來表示這種依賴 關系。
public class GuiceDemo extends RoboActivity {
@InjectView (R.id.hello) TextView helloLabel;
@Inject IGreetingService greetingServce;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
helloLabel.setText(greetingServce.getGreetings());
}
}
使用RoboGuice 的Activity需要從RoboActivity派生(RoboActivity 為Activity的子類).
使用@Inject標注greetingServce依賴於 IGreetingService服務
使用@InjectView表示helloLabel 依賴於R.id.hello (XML)
代碼中沒有創建greetingServce 對象的代碼(如 new xxx()) 和為helloLabel 賦值的代碼。這些值都可以Roboguice 自動創建和賦值注入 (Inject)到變量中。
為了說明問題,我們在代碼中添加兩個對 getGreetings的實現,一個為HelloWorld, 一個為HelloChina:
public
class HelloChina implements IGreetingService{
@Override
public String getGreetings() {
return "Hello,China";
}
}
public class HelloWorld implements IGreetingService{
@Override
public String getGreetings() {
return "Hello,World";
}
}
 android窗口管理框架簡介
android窗口管理框架簡介
窗口管理是android的一個核心內容。它管理著窗口的創建和銷毀,布局和大小,焦點的控制等等。窗口可以分為兩類:一種是應用窗口,即由具體應用創建的窗口,其實其中還可以細分
 Android的Activity(活動) 詳解
Android的Activity(活動) 詳解
Activity表示一個屏幕, 至少包含一個處理應用程序的主界面屏幕, 可以由多個fragments組成.創建一個Activity, 需要繼承一個Activity類, 首
 Android自定義View之繪制音樂播放器示波器
Android自定義View之繪制音樂播放器示波器
周末玩的有點嗨,沒更新博客了,今天補上,這個示波器是在大學的時候老師教的,但是出來工作一直沒有用到過,漸漸的也就忘記了,現在重新學習一下。來看看效果圖:這裡是一個自定義的
 Android開發環境配置完成
Android開發環境配置完成
最近對Google開發的開源智能手機操作系統Android比較感興趣,因此根據網上的資料下載了Eclipse,Android SDK3.0,並根據提示的步驟進行了環境的配