編輯:Android開發教程
一個Android應用程序中一般都有不止一個的Activity,這多個Activity之間 要相互通信和傳遞數據或者從一個Activity跳轉到另一個Activity。這樣才能使 得一個應用程序可以有豐富的功能和多元化的界面。
Activity傳遞數據和相互跳轉需要用到Intent對象。Intent在Android程序中 有很多的用途。我們現在主要關注它在兩個Activity之間通信所起的作用。簡單 地說Intent就是Android對象提供的Activity之間傳遞數據和操作指令的載體。 Intent負責對應用中一次操作的動作、動作涉及數據、附加數據進行描述, Android則根據此Intent的描述,負責找到對應的組件,將 Intent傳遞給調用的 組件,並完成組件的調用。一個Intent對象包含了一組信息,主要包含以下信息 :
1.Componetname 指定Intent的的目標組件的類名稱(即指定要啟動的 Activity的名稱)
2.Action 指定要啟動的組件要執行什麼樣的操作
3.Data 執行動作要操作的數據
4.Category 被執行動作的附加信息
5.Extras 其它所有附加信息的集合,主要是一些鍵值對,在一個Activity中 定義,通過Intent傳遞到另一個Activity中
6.flags 標志指示Android系統如何去啟動一個Activity
下面通過例子來說明在兩個Activity中間怎麼使用Intent對象。
程序的主 要流程為:在Activity01中有一個Button按鈕,為這個Button按鈕添加一個點擊 事件監聽器,當我們點擊這個Button時,觸發單擊事件。在事件的代碼沖我們頂 一個Intent對象,通過Intent對象的setIntent方法指定Componentname,並且在 Activity01中傳遞一個鍵為value,值為“傳遞的字符串參數”的string給 OtherActivity。然後啟動OtherActivity,在OtherActivity中的TextView控件 中顯示傳遞的這個string參數。
新建一個項目Activity_Intent。在項目中創建一個名為Activity01的的 Activity對象。在Activity01的布局文件編寫xml代碼使得Activity01只有一個 Button按鈕。
Activity01.java
01.package org.idea.android;
02.import android.app.Activity;
03.import android.content.Context;
04.import android.content.Intent;
05.import android.os.Bundle;
06.import android.view.View;
07.import android.widget.Button;
08.import android.widget.TextView;
09.import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
10.public class Activity01 extends Activity {
11. /** Called when the activity is first created. */
12. @Override
13. public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
14. super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
15. setContentView(R.layout.main);
16. Button button=(Button)findViewById(R.id.myButton);
17. button.setText("點擊跳轉到另一個Activity");
18. button.setOnClickListener(new buttonOnClickListener());//為button注冊單擊事件監聽器
19. }
20. class buttonOnClickListener implements OnClickListener {
21. @Override
22. public void onClick(View v) {
23. // TODO Auto-generated method stub
24. Intent intent=new Intent();//定義Intent對象
25. intent.setClass(Activity01.this,OtherActivity.class);//指定componentname
26. intent.putExtra("value", "傳遞的字符串參數");//傳遞鍵值對
27. Activity01.this.startActivity(intent);//啟動其它的Activity
28. }
29. }
30.}
main.xml
01.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 02.<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 03. android:orientation="vertical" 04. android:layout_width="fill_parent" 05. android:layout_height="fill_parent" 06. > 07.<Button 08. android:id="@+id/myButton" 09. android:layout_width="fill_parent" 10. android:layout_height="wrap_content" 11. /> 12.</LinearLayout>
 android源碼出現的@字符代表什麼意思
android源碼出現的@字符代表什麼意思
1.背景在android源碼中我們能看到各種以@開頭的字符,他們大多出現在注釋中,如下圖所示但是可不要小看了它們地作用,昨天當我編譯源碼的時候,就在一個“@l
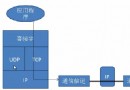 Android中如何實現Socket大文件斷點上傳
Android中如何實現Socket大文件斷點上傳
什麼是Socket?所謂Socket通常也稱作“套接字”,用於描述IP地址和端口,是一個通信連的句柄,應用程序通常通過“套接字&rdq
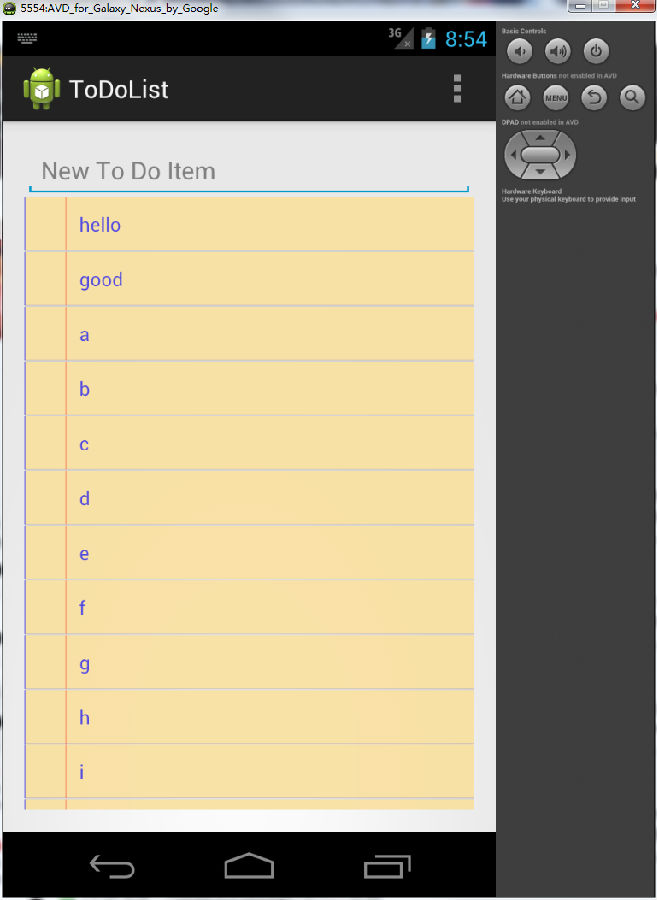 Android中的ToDoList(定制樣式) 詳解
Android中的ToDoList(定制樣式) 詳解
Android允許從已有的視圖工具箱(Widget Tool Box)派生子類 或 實現自己的視圖控件;通過重寫事件處理程序 和onDraw()方法, 但是仍然回調超類(
 在Android中實現360手機衛士懸浮窗效果
在Android中實現360手機衛士懸浮窗效果
大家好,今天給大家帶來一個仿360手機衛士懸浮窗效果的教程,在開始之前請允許我說幾句不相干的廢 話。不知不覺我發現自己接觸Android已有近三個年頭了,期間各種的成長少