編輯:安卓省電與加速
現在手機上的懸浮窗應用越來越多,對用戶來說,最常見的懸浮窗應用就是安全軟件的懸浮小控件,拿360衛士來說,當開啟懸浮窗時,它是一個小球,小球可以拖動,當點擊小球出現大窗體控件,可以進行進一步的操作如:釋放手機內存等等。於是借著慕課網的視頻,仿著實現了360加速球,增加了點擊小球進行釋放內存的功能。
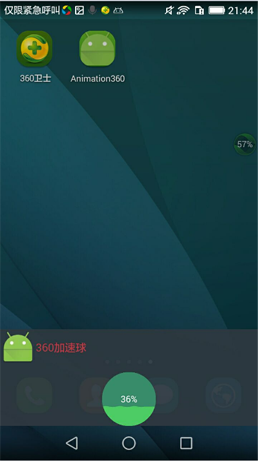
由於是手機只有頻幕截圖:實現後如下圖所示:點擊開啟按鈕,出現懸浮窗小球控件上面顯示手機的可用內存百分比;當拖動小球時,小球變為Android圖標;松開小球,小球依附在頻幕兩側;點擊小球,手機底部出現大窗體控件,點擊裡面的小球,進行手機內存的釋放;點擊手機屏幕的其他區域,大窗體消失,小球重新出現。
效果如下:

接下來就是實現的一些重要步驟:
1.FloatCircleView的實現(自定義view)
實現FloatCircleView的過程就是自定義view的過程。1、自定義View的屬性 2、在View的構造方法中獲得我們自定義的屬性 3、重寫onMesure 4、重寫onDraw。我們沒有自定義其他屬性所以省了好多步驟。
各種變量的初始化,設置拖動小球時要顯示的圖標,已經計算各種內存。(用於顯示在小球上)
public int width=100;
public int heigth=100;
private Paint circlePaint;//畫圓
private Paint textPaint; //畫字
private float availMemory; //已用內存
private float totalMemory; //總內存
private String text; //顯示的已用內存百分比
private boolean isDraging=false; //是否在拖動狀態。
private Bitmap src;
private Bitmap scaledBitmap; //縮放後的圖片。
/**
* 初始化畫筆以及計算可用內存,總內存,和可用內存百分比。
*/
public void initPatints() {
circlePaint = new Paint();
circlePaint.setColor(Color.CYAN);
circlePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
textPaint = new Paint();
textPaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
textPaint.setTextSize(25);
textPaint.setFakeBoldText(true);
textPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
//設置圖片
src = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
//縮放後的圖片(將圖標設置的和懸浮小球一樣大小。)
scaledBitmap = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(src, width, heigth, true);
//計算已用內存,總內存,已用內存百分比,
availMemory= (float) getAvailMemory(getContext());
totalMemory= (float) getTotalMemory(getContext());
text=(int)((availMemory/totalMemory)*100)+"%";
}
onMeasure();就是將固定的寬高寫死,通過 setMeasuredDimension(width, heigth);傳入。
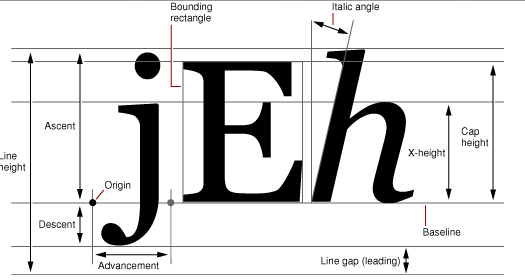
onDraw();進行懸浮小球繪制。定義一個boolean變量判斷當前狀態是否為拖動小球狀態,如果是拖動小球狀態,就在該位置繪制android圖標,如果不是拖動狀態,就進行小球繪制。畫小球沒有難度,關鍵是畫字。下面的2個圖可以加深對畫字時的理解。
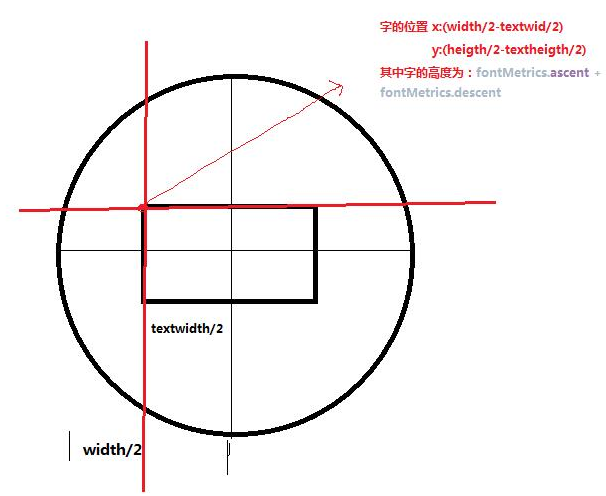
1.畫字時的x坐標(1.textPaint.measureText(text);得到字的寬度2.小球的寬度/2-字的寬度/2。)
2.畫字時的y坐標(1.Paint.FontMetrics fontMetrics = textPaint.getFontMetrics();得到字體屬性測量類。2.(fontMetrics.ascent + fontMetrics.descent) / 2 得到字的高度。3.小球的高度/2-字體的高度/2)
畫個圖就很好理解了:
/**
* 畫小球及文字。如果小球是在拖動狀態就顯示android圖標,如果不是拖動狀態就顯示小球。
* @param canvas
*/
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
if (isDraging){
canvas.drawBitmap(scaledBitmap,0,0,null);
}else {
//1.畫圓
canvas.drawCircle(width / 2, heigth / 2, width / 2, circlePaint);
//2.畫text
float textwidth = textPaint.measureText(text);//文本寬度
float x = width / 2 - textwidth / 2;
Paint.FontMetrics fontMetrics = textPaint.getFontMetrics();
float dy = -(fontMetrics.ascent + fontMetrics.descent) / 2;
float y = heigth / 2 + dy;
canvas.drawText(text, x, y, textPaint);
}
}
獲得手機已用內存及總內存的方法:
public long getAvailMemory(Context context)
{
// 獲取android當前可用內存大小
ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
ActivityManager.MemoryInfo mi = new ActivityManager.MemoryInfo();
am.getMemoryInfo(mi);
//mi.availMem; 當前系統的可用內存
//return Formatter.formatFileSize(context, mi.availMem);// 將獲取的內存大小規格化
return mi.availMem/(1024*1024);
}
public long getTotalMemory(Context context)
{
String str1 = "/proc/meminfo";// 系統內存信息文件
String str2;
String[] arrayOfString;
long initial_memory = 0;
try
{
FileReader localFileReader = new FileReader(str1);
BufferedReader localBufferedReader = new BufferedReader(
localFileReader, 8192);
str2 = localBufferedReader.readLine();// 讀取meminfo第一行,系統總內存大小
arrayOfString = str2.split("\\s+");
for (String num : arrayOfString) {
Log.i(str2, num + "\t");
}
initial_memory = Integer.valueOf(arrayOfString[1]).intValue() * 1024;// 獲得系統總內存,單位是KB,乘以1024轉換為Byte
localBufferedReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
//return Formatter.formatFileSize(context, initial_memory);// Byte轉換為KB或者MB,內存大小規格化
return initial_memory/(1024*1024);
}
2.創建WindowManager窗體管理類,管理懸浮小球和底部大窗體。
WindowManager類。用來管理整個懸浮小球和手機底部大窗體的顯示和隱藏。
必須在Manifest文件中增加<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW" />權限。
通過 WindowManager wm = (WindowManager)getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);獲取窗體管理類;
利用wm.addView(view, params);將view增加到窗體中。
利用wm.remove(view,params);將view從窗體中移除。
利用wm.updateViewLayout(view,params);來更新view.
WindowManager.LayoutParams用來設置view的各種屬性。
1.創建FloatViewManager實例。
//單例模式創建
public static FloatViewManager getInstance(Context context){
if (inStance==null){
synchronized(FloatViewManager.class){
if (inStance==null){
inStance=new FloatViewManager(context);
}
}
}
return inStance;
}
2.展示懸浮小球和展示底部窗體的方法。(展示窗體的方法同展示懸浮小球類似。)
/**
* 展示浮窗
*/
public void showFloatCircleView(){
//參數設置
if (params==null){
params = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
//寬高
params.width=circleView.width;
params.height=circleView.heigth;
//對齊方式
params.gravity= Gravity.TOP|Gravity.LEFT;
//偏移量
params.x=0;
params.y=0;
//類型
params.type=WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_TOAST;
//設置該window屬性。
params.flags= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL;
//像素格式
params.format= PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
}
//將小球加入窗體中。
wm.addView(circleView, params);
}
public void showFloatCircleView(){
......
}
3.當啟動程序,首先創建懸浮小球,小球可以拖拽,點擊小球,手機底部窗體顯示(FloatMenuView),小球隱藏。所以,對小球(circleView)要對其進行setOnTouchListener和setOnClickListener事件監聽。
分析小球的事件分發; 對於小球:
當ACTION_DOWN時,記錄小球的downX,downY,以及startX,startY,
當ACTION_MOVE時,將circleView是否拖拽狀態置為true,記錄小球的moveX,moveY,計算小球移動的距離(dx,dy),然後根據 wm.updateViewLayout(circleView,params);更新小球位置。最後將最後move的坐標賦值給startX,startY。
當ACTION_UP時,將circleView是否拖拽置為false,記錄抬起時的坐標,upx,根據upx和手機屏幕寬度/2,進行判斷,來覺得最終小球是貼在屏幕左側,還是右側。後面為小球拖拽的誤差。當小球拖拽的距離小於10個像素時,可以觸發小球的點擊事件。(小球的Touch事件,優先於小球的點擊事件,當Touch事件返回true時,此事件被消費,不再向下傳遞事件。當Touch事件返回false時,此事件繼續向下傳遞,從而觸發小球的點擊事件。)
小球的點擊事件:點擊小球,懸浮小球隱藏,手機底部窗體出現。並設置有底部窗體出現時的過渡動畫。
//給circleView設置touch監聽。
private View.OnTouchListener circleViewOnTouchListener=new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
//最後按下時的坐標,根據ACTION_MOVE理解。
startX = event.getRawX();
startY = event.getRawY();
//按下時的坐標。
downX = event.getRawX();
downY = event.getRawY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
circleView.setDrageState(true);
moveX = event.getRawX();
moveY=event.getRawY();
float dx = moveX -startX;
float dy=moveY-startY;
params.x+=dx;
params.y+=dy;
wm.updateViewLayout(circleView,params);
startX= moveX;
startY=moveY;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
float upx=event.getRawX();
if (upx>getScreenWidth()/2){
params.x=getScreenWidth()-circleView.width;
}else {
params.x=0;
}
circleView.setDrageState(false);
wm.updateViewLayout(circleView,params);
if (Math.abs(moveX-downX)>10){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
default:
break;
}
return false;
}
};
circleView.setOnTouchListener(circleViewOnTouchListener);
circleView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//Toast.makeText(, "onclick", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
//隱藏circleView,顯示菜單欄。
wm.removeView(circleView);
showFloatMenuView();
floatMenuView.startAnimation();
}
});
3.MyProgreeView(手機底部窗體中小球的實現)。
1.初始化畫筆,對view進行手勢監聽。監聽單擊和雙擊事件。(必須設置view是可以點擊的)
private void initPaint() {
//畫圓畫筆
circlepaint = new Paint();
circlepaint.setColor(Color.argb(0xff, 0x3a, 0x8c, 0x6c));
circlepaint.setAntiAlias(true);
//畫進度條畫筆
progerssPaint = new Paint();
progerssPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
progerssPaint.setColor(Color.argb(0xff, 0x4e, 0xcc, 0x66));
progerssPaint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN));//繪制重疊部分
//畫進度畫筆
textPaint = new Paint();
textPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
textPaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
textPaint.setTextSize(25);
//畫布
bitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(width, heigth, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
bitmapCanvas = new Canvas(bitmap);
//手勢監聽。
gestureDetector = new GestureDetector(new MyGertureDetectorListener());
setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return gestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
});
//設置view可以點擊。
setClickable(true);
}
class MyGertureDetectorListener extends GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener{
@Override
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
......
//雙擊事件的邏輯
return super.onDoubleTap(e);
}
@Override
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e) {
......
//單擊事件的邏輯
return super.onSingleTapConfirmed(e);
}
}
2.用handler交互進行單擊和雙擊事件的狀態更新。單擊時,利用貝塞爾曲線,實現波紋蕩漾效果。雙擊時,波紋不斷下降,進行內存釋放,最後顯示內存釋放後的已用內存百分比。handler發送周期消息,讓單擊事件和雙擊事件的小球不斷進行重繪。(重繪在下一小節講)。
//單擊事件發送周期handler.
private void startSingleTapAnimation() {
handler.postDelayed(singleTapRunnable,200);
}
private SingleTapRunnable singleTapRunnable=new SingleTapRunnable();
class SingleTapRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
count--;
if (count>=0) {
invalidate();//不斷進行重繪。
handler.postDelayed(singleTapRunnable,200);
}else {
handler.removeCallbacks(singleTapRunnable);
count=50;
}
}
}
//雙擊事件發送周期handler。
private void startDoubleTapAnimation() {
handler.postDelayed(runnbale,50);
}
private DoubleTapRunnable runnbale=new DoubleTapRunnable();
class DoubleTapRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
num--;
if (num>=0){
invalidate();//不斷進行重繪。
handler.postDelayed(runnbale,50);
}else {
handler.removeCallbacks(runnbale);
//釋放內存。
killprocess();
//計算釋放後的已用內存百分比。
num=(int)(((float)currentProgress/max)*100);
}
}
}
3.單擊事件和雙擊事件的重繪。
首先是小球的繪制,和波紋路徑的繪制。
//繪制小球
bitmapCanvas.drawCircle(width / 2, heigth / 2, width / 2, circlepaint);
//根據path,繪制波紋路徑。每次繪制前將上次的path,reset.
path.reset();
float y =(1-(float)num/100)*heigth;
path.moveTo(width, y);
path.lineTo(width, heigth);
path.lineTo(0, heigth);
path.lineTo(0, y);
接著利用貝塞爾曲線將波紋路徑繪制。
Android-貝塞爾曲線
貝塞爾曲線在android中的應用
這裡有詳細的講解貝塞爾曲線。其實不需要深入的理解。只要知道能用它來實現水波紋效果就行了(貝塞爾曲線用處很多,翻書效果也可以用它實現。)主要利用 path.rQuadTo(x1,y1,x2,y2); 終點(x2,y2),輔助控制點(x1,y1)的貝塞爾曲線。因此,通過不斷改變y1的位置,我們可以繪制出水波紋的效果。
首先判斷它是否為雙擊擊事件:
若是雙擊:設置一個變量d,通過不斷改變d的值(d的值的改變由num引起,而num實在handler中不斷減小的。num–;),來繪制貝塞爾曲線。實現水波紋的下降效果。
若是單擊:設置一個count值,通過不斷改變count值(count值的改變是在handler中實現的。count–;),首先判斷count是否能被2整除,交替繪制這兩條貝塞爾曲線。(這兩條貝塞爾曲線正好相反),從而實現水波蕩漾的效果。
(用for循環是實現水波的波數,一對path.rQuadTo();只能實現一次波紋。可以自己去驗證)
if (!isSingleTap){
float d=(1-(float)num/(100/2))*10;
for (int i=0;i<3;i++){
path.rQuadTo(10,-d,20,0);
path.rQuadTo(10,d,20,0);
}
}else {
float d=(float)count/50*10;
if (count%2==0){
for (int i=0;i<=3;i++){
path.rQuadTo(10,-d,30,0);
path.rQuadTo(10,d,30,0);
}
}else {
for (int i=0;i<=3;i++){
path.rQuadTo(10,d,30,0);
path.rQuadTo(10,-d,30,0);
}
}
}
最後是釋放內存的方法。記得要在Manifest文件中增加<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.KILL_BACKGROUND_PROCESSES"/>權限。
public void killprocess(){
ActivityManager activityManger=(ActivityManager) getContext().getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
List<ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo> list=activityManger.getRunningAppProcesses();
if(list!=null)
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++)
{
ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo apinfo=list.get(i);
String[] pkgList=apinfo.pkgList;
if(apinfo.importance>ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo.IMPORTANCE_SERVICE)
{
// Process.killProcess(apinfo.pid);
for(int j=0;j<pkgList.length;j++) {
boolean flag=pkgList[j].contains("com.example.yyh.animation360");//這裡要判斷是否為當前應用,要不然也可能會結束當前應用。
if(!flag){
activityManger.killBackgroundProcesses(pkgList[j]);
}
}
}
}
4.FloatMenuView的實現。
1.創建一個float_menuview.xml;其中包括一個ImageView+TextView+自定義的MyProgreeView。
底部窗體要被設置能被點擊。android:clickable="true";
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#33000000"
>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#F02F3942"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:id="@+id/ll"
android:clickable="true"
>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="15sp"
android:textColor="#c93944"
android:text="360加速球"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<com.example.yyh.animation360.view.MyProgreeView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
2.將FloatMenuView 根據條件,利用(wm.addView(view, params);將view增加到窗體中。
利用wm.remove(view,params);將view從窗體中移除。)方法,進行底部窗體view的顯示和隱藏
TranslateAnimation類用來設置底部窗體進入時的動畫效果。TranslateAnimation(int fromXType,float fromXValue,int toXType,float toXValue,int fromYType,float fromYValue,int toYType,float toYValue)
int fromXType:x軸方向起始的參照值有3個選項。(1.Animation.ABSOLUTE:具體的坐標值,指絕對的屏幕像素單位。
2.Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF:相對自己的坐標值。3.Animation.RELATIVE_TO_PARENT:相對父容器的坐標值。)
float fromXValue 第二個參數是第一個參數類型的起始值(例如若第一個參數設置為Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,第二個參數為0.1f,就表示為自己的坐標值乘以0.1);
int toXType:x軸方向終點的參照值有3個選項同第一個參數。
float toValue:第四個參數是第三個參數類型的起始值。
Y軸方向的參數同理。起點+終點;(每個參數後一個參數為前一個參數的起始值。)
並對此view設置OnTouchListener,OnTouch事件最後必須返回false,表示此事件仍然需要向下傳遞。從而實現點擊手機其他區域時,手機底部窗體隱藏,懸浮小球顯示,點擊底部窗體時無變化,點擊底部窗體中的小球時,觸發其單擊和雙擊事件。
View view =View.inflate(getContext(), R.layout.float_menuview,null);
LinearLayout linearLayout= (LinearLayout) view.findViewById(R.id.ll);
translateAnimation = new TranslateAnimation(Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0,Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0,Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,1.0f,Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0);
translateAnimation.setDuration(500);
translateAnimation.setFillAfter(true);
linearLayout.setAnimation(translateAnimation);
view.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
FloatViewManager manager=FloatViewManager.getInstance(getContext());
manager.hideFloatMenuView();
manager.showFloatCircleView();
return false;
}
});
addView(view);
5.MyFloatService
用來創建FloatVIewManager單例,管理懸浮小球+手機底部窗體的創建和移除。
public class MyFloatService extends Service {
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
//用來開啟FloatViewManager
FloatViewManager manager=FloatViewManager.getInstance(this);
manager.showFloatCircleView();
super.onCreate();
}
}
6.MainActivity的實現
定義一個intent,開啟服務(在服務中創建WindowManager單例對象,進行懸浮小球和手機底部窗體的管理。),關閉當前的activity。
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
public void startService(View view){
Intent intent=new Intent(this, MyFloatService.class);
startService(intent);
finish();
}
}
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 android自定義組件(手機加速球+水面波動效果)
android自定義組件(手機加速球+水面波動效果)
先看效果本項目實現起來大體上我們分三步講解【1】水面波動效果實現代碼首先畫出波浪線,通過通過貝塞爾曲線 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
 安卓手機怎麼加速?安卓手機加速教程
安卓手機怎麼加速?安卓手機加速教程
目前,安卓系統的手機是最受歡迎的手機,也是目前使用人數最多的手機。只是,安卓系統的智能手機都有一個共同的特點,那就
 Android安卓手機省電技巧
Android安卓手機省電技巧
筆者個人的省電方式主要有兩種:1.不獲取手機最高權限的“屌絲”省電法。2.獲取ROOT最高權限,給手機做大手術最到極致省電方法。要記得一點,手機廠
 OPPO Find7省電模式設置方法
OPPO Find7省電模式設置方法
OPPO Find7手機省電模式如何開啟?這省電模式對於用戶來說幫助還是很大的,那麼這開啟方式又是什麼呢?一起來看